About 5000 armored vehicles 1948-Present
Tanks
Prototypes & Projects
The Swiss Army
Since the constitution of the Bundesheer in 1848 (Federal Army) and then a reduction to Cantonal forces, the Swiss Army is an oddity for a strongly federal, neutral country with mandatory conscription. It is a citizen army, whereas other nations are now acquired to the idea of a small professional standing army and a corps of reservist. A position of fierce independence kept with the central powers during ww1, and still kept during ww2. During this time, the Swiss were never threatened by the Axis, because of an ambivalent rôle, notably on the economical side.
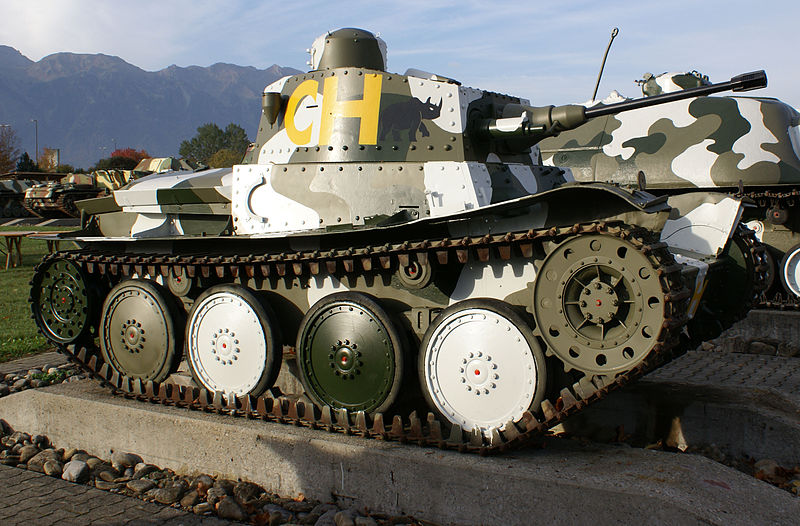

Swiss Panzerwagen 39 (Czech LTH) before ww2, now preserved at Thun museum
But it was also a haven for all those who flied persecutions, resisters, deserters, and spies. However there had been regular concerns by pacifists and leftist political side to suppress the army due to a bad image acquired first against the miners of the Gotthard tunnel in 1871, and later in the worker’s repression of 1918 following a general strike, and again after a rather violent reprisal against rioters involved an anti-fascist demonstrations in Geneva in 1932. WW2 saw the third largest mobilization of the Swiss conscripts and reserves, under command of Henri Guisan.
The Swiss Army in WW2
The history of armoured warfare in Switzerland could be traced to the adoption of the French Renault FT as its first tank, only five vehicles that entered service in 1921. In 1931, eight Vickers-Carden-Loyd were also acquired, followed by a single Landsverk L60 for testings in 1936. By 1939, the Swiss Army had 24 Panzer 39, Czech tanks purchased with properly Swiss modifications and based on the LTL-H. 12 Hotchkiss H35 were also purchased in addition. With these feeble forces, the Swiss federation had to face a potential force of many Panzerdivisions that could he been detached for any invasion on the shortest notice. Hitler however never seriously planned an invasion of Switzerland, although there were several concerns about him seen in the Swiss press as a warmonger, vigorously criticizing the the third Reich whereas Hitler saw Switzerland as a medieval rudiment of “renegade Germans”.
The Swiss Army long considered an invasion of the country and several lines of defences, complete with bunkers and pillboxes, artillery and observation points dotted the landscape on any possible direction. It was envisioned to deter any enemy with 80 000 well trained conscripts which perfectly well knew the country and used at best any natural and artificial defence this mountainous terrain can offer. Panzers would be indeed not very useful and the fight would have to be done mostly by alpine troops which were in short supply, already serving in the Balkans, Norway and the Caucasus.
There were numerous flight violations of the Swiss airspace by the Luftwaffe in may-june 1940, ans the Swiss air force retaliated, downing 11 aircrafts. During the war from 1943 to 1945, many allied airmen whose bombers were damaged preferred to crash in Switzerland rather to became POWs in Germany. Crews were indeed well treated, generally housed in deserted ski resorts, waiting to join Great Britain through clandestine ways. However this changed when allied bombers mistook Schaffhausen on the border to Ludwigshafen am Rhein, 300 km away. A virulent press was followed by a “zero-tolerance” policy, which implied that any allied violation of the Swiss airspace would be met with the same resistance as for axis planes. That did not prevented later other mistakes, in Stein am Rhein, Vals, and Rafz, but also in Basel and Zurich in 1945. In 1944, the Swiss army built and tested a tank-hunter, the Nahkampfkanone-1, based on the Panzerwagen 39 or type LTL-H chassis, followed in 1946 by the Nahkampfkanone-2 Gustav, inspired by the Hetzer.
Cold War
By far, in 1947, the bulk of Swiss tank force was made of brand new 158 Panzerjäger G 13s (postwar czech-built Jagdpanzer 38 Hetzers called Praga ST-I, ST-III), only removed from service in 1973. They made the delight of private collections. This prime force was completed by 200 AMX-13s (Leichtpanzer 51) purchased from France in 1954, and retired in 1980. In 1952, two M47 Patton were acquired for tests, but no order was placed. Switzerland was not part of NATO then, but being neutral and bordered by allied countries, maintained its traditional army structure, based on defending areas in depth, backed by a “national redoubt” made of well-stockpiled positions high in the Alps.

Panzer 55/57 MBT (Centurion in Swiss service).
But in 1961, it was reformed as the “Armee 61”, along with a new organization. This army comprised the Field Army Corps 1, 2, and 4, and the Mountain Army Corps 3. Since 1956 when the funds were given by the federal parliament time, a new type of national tank was developed by Eidgenössische Konstruktionswerkstätte Thun. The Panzer 58 entered service in 1958 and equipped with a British Ordnance QF 20 pounder, but rearmed in 1960-62 by a L7 105 mm. The next Panzer 61 was based on the model 58, but up-armoured and more powerful. The Panzer 68 looked identical but was improved in many aspects. In total, 10 preserie panzer-58, 150 panzer-61 and 390 Panzer-68 of all versions were built. They formed the bulk of the confederation’s army until the late 1970s alongside 312 Panzer 55/57 and 67 which were local denominations of the British Centurion tank.
By the fall of the 1980s, replacement of these tanks was realized by the funding of a purchase of West German Leopard 2A4, renamed in Swiss service Panzer-87. No less than 380 were in service by the 1990s, but this figure was reduced after 2004 to 224, including 134 upgraded to the WE standard. Light armoured vehicles were British Universal Carriers, the M113 APC (purchased in large quantities), and the M548 snow APC. Saurer and Mowag presented prototype competing against the M113 but lost. However Mowag was to become one of the major supplier of APCs and wheeled vehicles for the Swiss army in the 1980s-1990s, most notably with the Mowag Piranha. Self propelled artillery was secured by the purchase of 577 M109 howitzer Panzerhaubitze 66. Other cold war vehicles included the Entpannungspanzer 56 (30 ARVs), Entpannungspanzer 65 ARV (69), Brückenpanzer 68 bridgelayer (30). Many vehicles were also tested, like the Panzerkanone 68 SPG or the Fliegerabwehrpanzer 68 SPAAG.
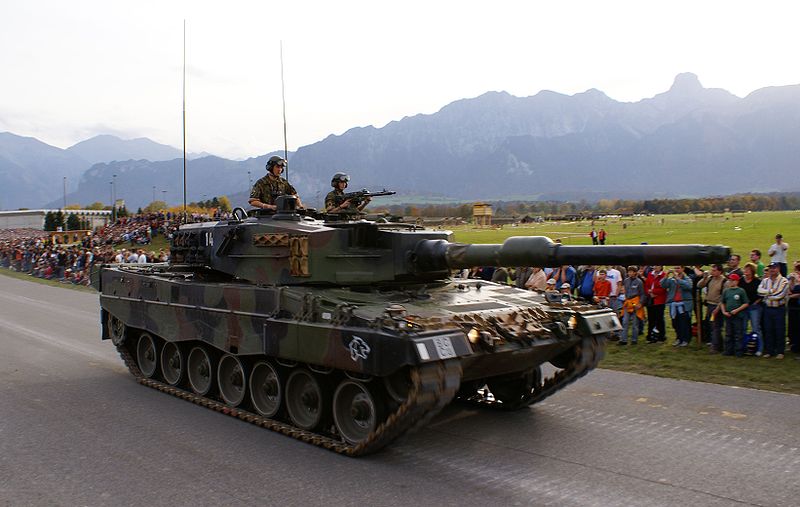

Panzer 87 (Leopard 2) at the Steel Parade in 2006
Variants of the Schützenpanzer 63 (M113 in Swiss service)
- Schützenpanzer 63 (basic M113A1)
- Schützenpanzer 63/73: Variant with front float panel+ Swedish Hagglunds turre/Oerlikon 20 mm 48/73.
- Schützenpanzer 63/89: Additional passive armor, 76 mm smoke grenade launchers, RISE powerpack.
- Kommando Schützenpanzer 63: Command variant, .50cal HMG
- Kommando Schützenpanzer 63/89: SPz 63/89 Command version, 20mm gun turret.
- Kranpanzer 63 (M579).
- Feuerleitpanzer 63: Improved command, fire control center for mobile artillery units.
- Feuerleitpanzer 63/98: Upgraded with INTAFF system.
- Geniepanzer 63: Bulldozer kit vehicle
- Minenwerferpanzer 64: M106A1 mortar carrier with a Thompson Brandt 120mm mortar – Minenwerferpanzer 64/91 upgrade
- Minenräumpanzer 63/00: Mineclearing vehicle, lightweight mine clearing ploughs.
- Übermittlungspanzer 63 – Signals vehicle
Infrastructures
Although there was already a net of fortifications spread inside the Swiss territory and the “national redoubt” in the Alps, the cold war saw a renew of underground constructions.
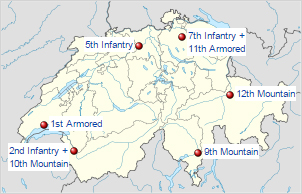
Swiss army brigades locations.
Post cold war (1990- today)
In the late 1980s there were concerns about the utility of the army and in 1989, a large referendum in november on this question, although defeated saw 35.6% of the population supporting the idea of a complete abolition. In 1995, new reforms saw the army reduced to 400 000 and reorganized once more as the Armee 95. Nowadays, this figure has been reduced even further, to just 134 886 according to the Armee XXI organization in 2004, most of it being a conscript reserve army, with a full professional core of 4230 including NCOs and only 1250 women in this total.
Due to several languages an agreement was found about the instruction in German. The XXI armee comprised the infantry brigades 2 and 5, mountain infantry brigades 9 and 12 and armoured brigades 1 and 11 with two large reserve brigade 7 and 10. There are Four territorial regions based on the Canton territories, responsible for the security in their region but under the overall command of the the Federal Council. Territorial region HQs are Morges (Vaud), Kriens, Altdorf and St. Gallen.
Links
The Swiss army on Wikipedia
Official webpage
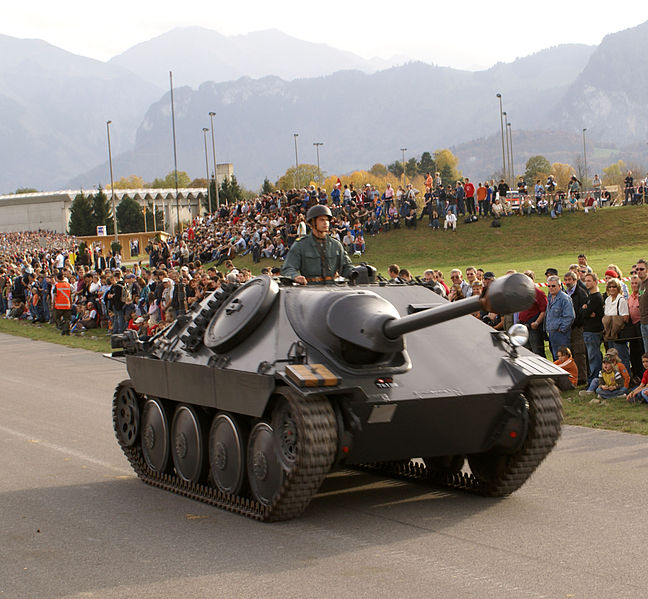

Swiss Panzerjäger G13 (1947)
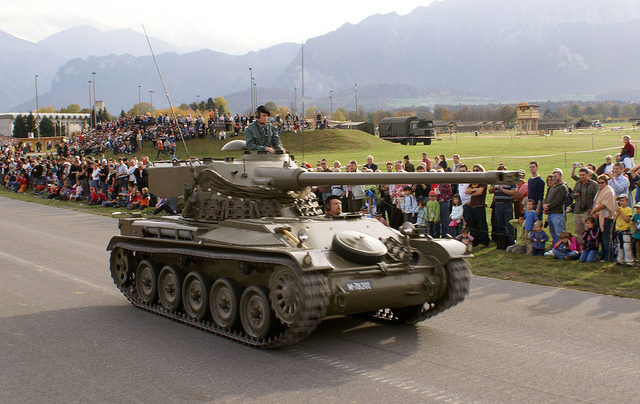

Swiss AMX-13 (Leichtpanzer 51)

Swiss M113 (Schützenpanzer 63) at the 2006 steel fest parade.
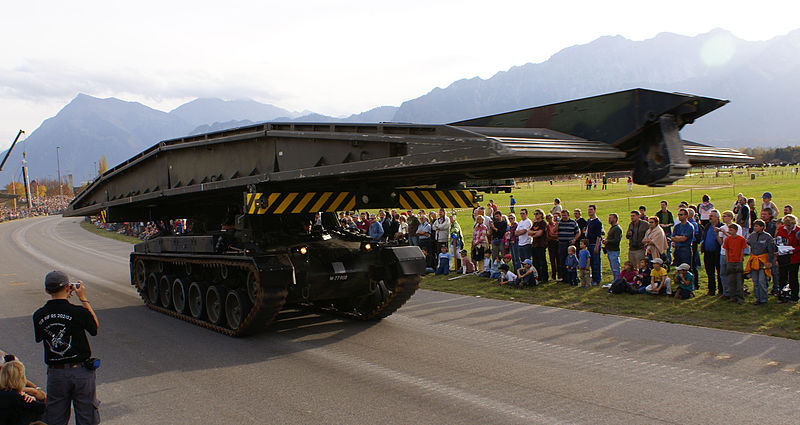

Brückenleger 68/88

Nahkampfkanone I tank hunter (1944) based on the Czech TNH

Nahkampfkanone II Gustav (1947)

Nahkampfkanone II Gustav (1947), another view.
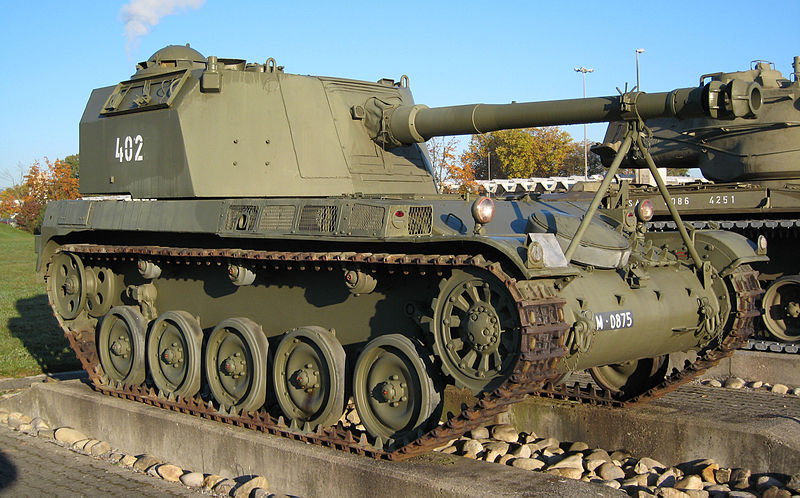

Panzerhaubitze AMX 13 SPG (4 built and tested) based on the AMX-13.
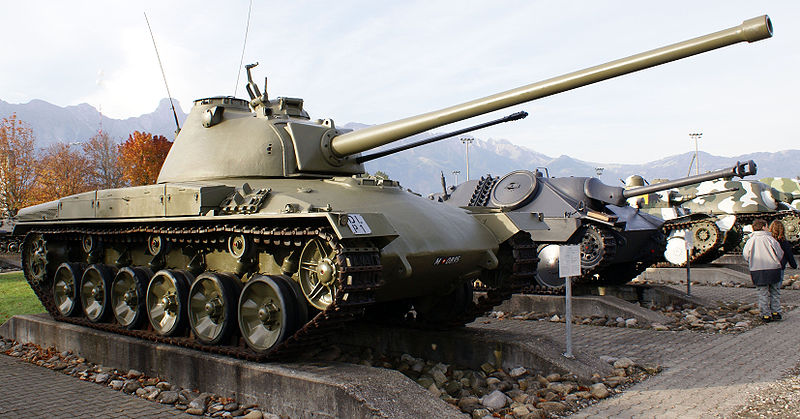

KampfPanzer 58, preserie (here the second prototype)
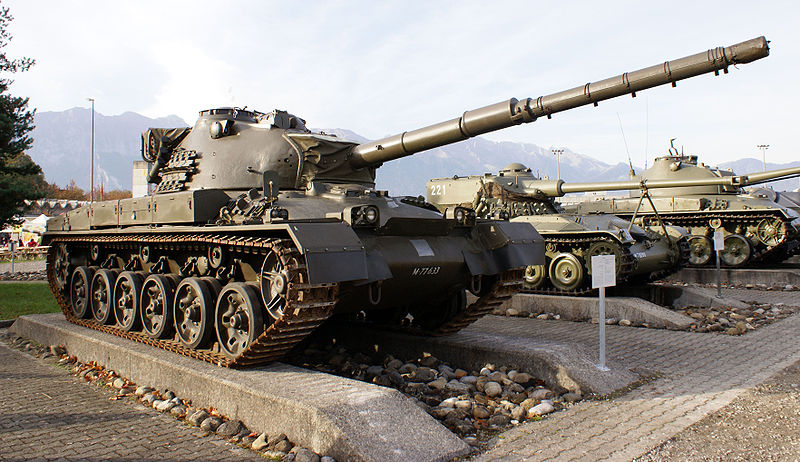

KampfPanzer 61 displayed at the Thun army museum

Kampfpanzer 68/88
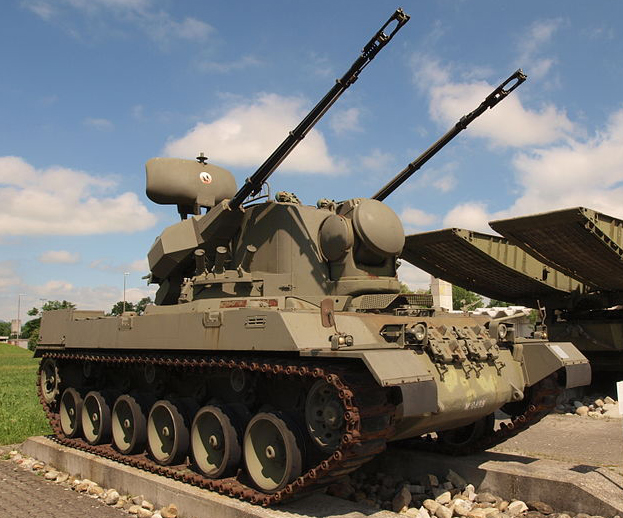

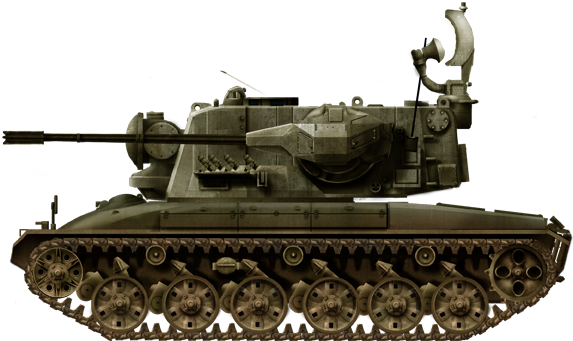
Fliegerabwehrpanzer-68 SPAAG. Experimental, two tested.

Zielpanzer-68 test tank for target practice, based on the Panzer 68 chassis (10 built).

MOWAG Piranha IIIC prototype APC

Saurer Tartaruga prototype APC
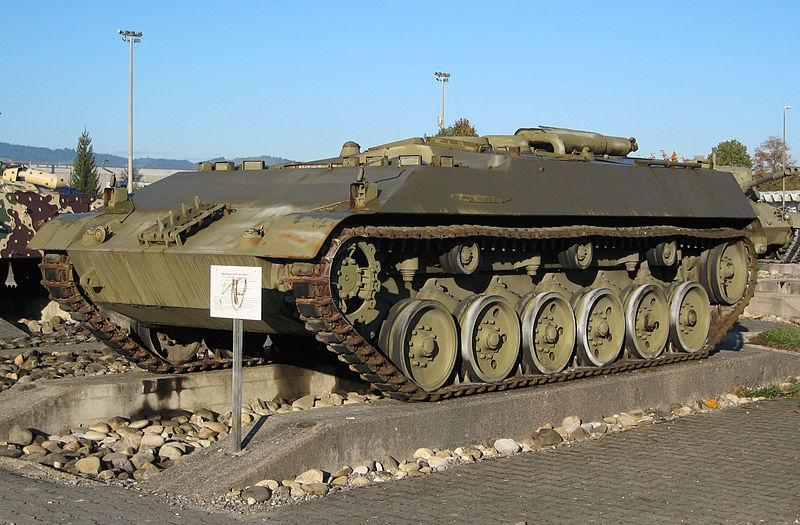

Mowag 3M1 Pirat prototype APC

MOWAG Shark, prototype APC
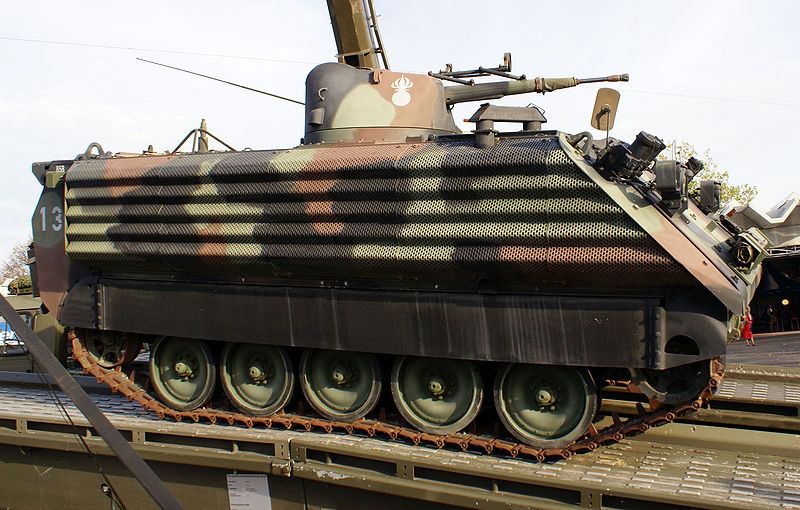

Schützenpanzer 63/89, upgraded version

Panzerkanone 68 SPG

Entpannungspanzer 65

The Mowag Shark was an attempt to produce an alternative to the traditional Piranha in 1981, developed on the basis of the 6×6 Mowag Puma (1981) and solely for the export market as a multiple weapon platform. Three prototypes only were built, the first one being showcased at the 1981 paris Air Show exhibition, armed with a Oerlikon-Bührle Type GDD-BOE twin 35 mm, in a SPAAG configuration. Later in 1982 it was tested in a tank hunter configuration with a French Fives-Gail Babcock FL-12 turret, 105 mm main gun and SOPTAC fire control system. It also tested in Germany the Rheinmetall 105 mm Rh 105-11 super low recoil gun (inside a turret also designed by Rheinmetall, able to fire all NATO ammunitions.
Eventually the early SPAAG was modified in 1983 to carry the Wildcat twin 30 mm SPAAG turret, and it was also tested in a SPAAML configuration with the French Crotale missile system (2×4 radar guided missiles), or the Swiss Air Defense Anti-Tank System (ADATS) and other configurations like the HOT missile tank hunter. The Mowag Shark was eventually never ordered and the Pirahna 10×10 gained most from this development. The welded steel construction was proven against the Soviet 14.5 mm KPV armor piercing rounds. The driver sat in the left front of the hull, and the the engine, transmission, and fuel tanks were relegated at the rear unlike APCs, leaving the whole central area free for the armament modules and fighting compartment. However an APC was also allegedly tested. The Mowag Shark was 7.52 m long, weighted 21 tons in battle order and was propelled by a Detroit Diesel 8V-71T turbo-charged diesel which developed 530 hp at 2500 rpm coupled to an Allison HT 750 transmission, giving a top speed on flat of 100 kph (60 mph).
Illustrations

Mittlerer Panzer 61, standardized in the 1960s.

Late Panzer 61 AA9, upgraded to the Panzer 68 standard and camouflaged, 1970s.

Panzer-68 serie I, 1971 in green livery

Serie 3 or AA3 in the 1980s

Panzer 68/88 wth the “grosser turm”, the major upgrade, in 1993.
Prototype of the Fliegerabwehrpanzer 68, 1979. This is a hasty photoshop. In fact the hull was quite different. This illustration will be updated soon.

Mowag Piranha IB 6×6 TOW (Panzerjager 90) of the Swiss Army in the 1980s.

Chilean Cardoen/FAMAE Piranha I.

Canadian licence-built AVGP Cougar.

Canadian licence-built AVGP Grizzly.

Australian licence-built 8×8 ASLAV.

Mowag APC90 of the Swiss Army.

Piranha II of the Omani Army with an Alvis 30 mm turret.

Saudi LAV-M (National Guard).
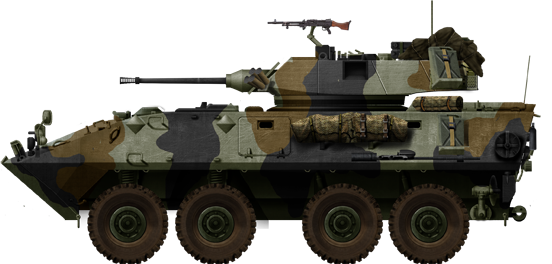
USMC LAV-25 (1983). Joint US-Canadian vehicle based on the Piranha II.

Canadian Bison APC (based on the Piranha II) (1988).
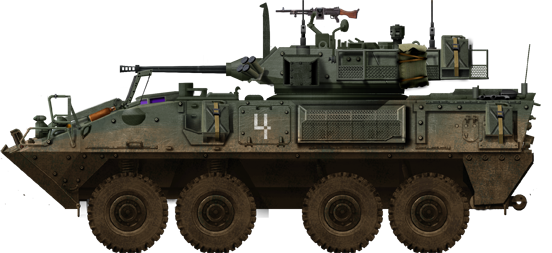
Canadian Coyote (based on the LAV-II) recce 8×8 (1996).

Qatari Piranha II CCTS-90 tank hunter (with a Belgian Cockerill 90 mm gun).

Irish Piranha IIIH.

Romanian Piranha IIIC.

Spanish Marines Piranha IIIC Command.

Belgian Piranha IIIC.

Danish Piranha IIIC APC in Afghanistan.
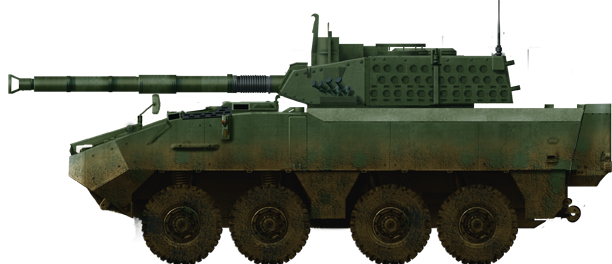
Belgian Piranha IIIC IFV with CMI turret and CTS Cockerill 90 mm gun.

Piranha III 10×10 tank hunter demonstrator for the middle east, armed with a French GIAT TML 105 mm turret.

US Army/USMC IAV Stryker or M1126 Infantry Carrier Vehicle (2002). The 105 mm armed M1128 Mobile Gun System (MGS) was developed over this platform.

Mowag Roland of the Mexican logistic battalion.

Roland ambulance.

Mowag Roland, Police vehicle.

Mowag MR8 SW2, the 20 mm armed version.

MR8 SW1 (Kfz91) version, the Bundesgrenzschutz unarmed APC.

