Forever associated with the gulf war in all medias, the cold war successor to the mythical Jeep went on a long way, dozens of years of development with many fathers. Born for the cold war, it was condemned by IEDs in the 2000s, and ultimately towards an uncertain fate as of today, despite many imitations round the world.
NOTE: This post is a placeholder for SEO purpose/ It does not represent the quality and depht of the final article
As Armored Personnel Carriers (APC) go, the M113 was the most produced tracked APC, at 88,000+. However, the most produced armored personal carrier is the Humvee. Unveiled in 1983, 280,000 vehicles have been built so far. It still comes in less than the iconic vehicle it replaced, the Jeep, of which 650,000 were made. The Humvee was produced to be fully enclosed and Nuclear (Radiation), Biological, Chemical (NBC) proof. The Jeep was never considered to be "armored" as it was an open cab vehicle. Conversely, the Humvee, up armored, is considered an armored fighting vehicle.
The utility and versatility of the vehicle was well proven after the end of the Cold War. A familiar sight in the Gulf wars and in Afghanistan, the Humvee was well-known and well-showcased by the world wide media, and became an iconic symbol of these conflicts, just as the Huey helicopter was to Vietnam. This is the quintessential modern U.S. "Battle Taxi", although this was not its primary objective or duty. The Humvee was largely exported and also inspired a wide range of civilian adaptations and applications.
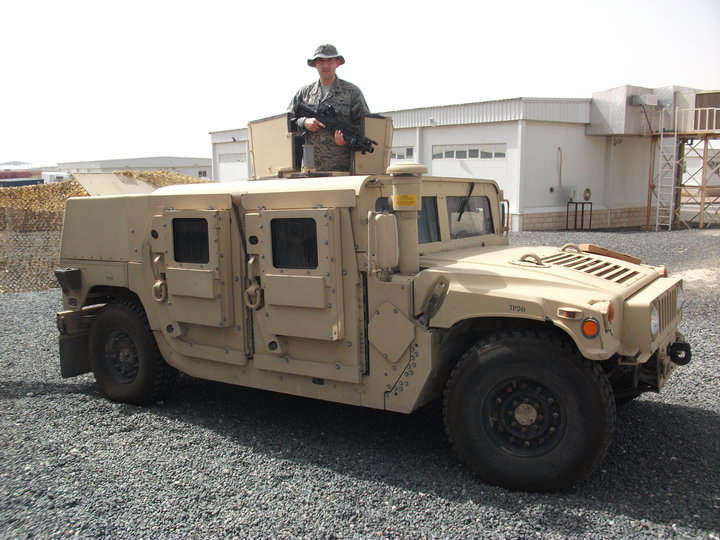

Humvee with a FRAG-6 reinforced add-on armor in April 2010
The Jeep design had one overarching flaw from its inception in 1939. There was no protection for the passengers. As the Cold War progressed, there was no protection for the Jeep crew in case of an NBC threat or against shrapnel and small arms fire. The original Jeep was open where crew can literally jump in and out. However, during combat (not infrequent as it was used for reconnoitering in enemy territory), the driver had to react quickly and retreat swiftly before the enemy could effectively return fire. A completely armored, encased body would had the advantage of offering this supplementary protection without loosing the "fast descent" characteristic of the older model.
The idea of fitting an open back where soldiers can quickly embark and disembark without bothering with doors or hatches, was perhaps something related to the deeply popular and deeply rooted affection of civilians for pickup trucks. This trade-off with NBC protection was relative as the main 4-seats compartment was still fully enclosed. The Humvee was not a traditional APC due to its size and primary duties of reconnaissance and liaison. However its stiff construction and size allowed to adapt a large variety of weapons that the Jeep could never mount. So when the vehicle was eventually unveiled, it was praised as indeed the only true possible successor of the vehicle created originally by Bantam in 1939.
The Cheetah was very much in its appearance a progenitor of the Humvee. It was a powerful true 4x4, not with a Lamborghini V12 as some stated but a better suited engine for military specs, the Chrysler 5.9 liter (360 ci) V8. It was waterproofed and rear-mounted, with a 3-speed gearbox. The reinforced fiberglass prototype was built at MTI in San Jose, California and then sent to Sant'Agata near Bologna where it was completed by Lamborghini. At more than 2 tons (4,502 lb) and with a rear engine, top speed was not the primary objective. The prototype was only showed once unofficially, and stored as AM General was later awarded the contract for a very similar vehicle. Lamborghini however tried later the LM002 of its own design, which never got passed the prototype stage and did not profit the already dwindling finances of the company following the first petrol crisis in the 1970s.
The final specifications for a High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle were drafted in 1979, originally to replace the 1/4 to 1 1/4-ton range M151 MUTT and M565 Gamma Goat. Paramount was the off-road performance, but also a large payload capacity and extensive armor protection against indirect fire. Another demand for the width was to fit inside standard cargo planes as well as European tunnels, bridges, and roadways. At the end it was far larger than the jeep and twice as heavy, with improved suspensions and a 410 mm ground clearance. Field performances expected were climbing a 60% slope or stay stable on a 40% slope, ford 5 ft (1.5 m) of water unprepared thanks to a snorkel air intake and electronics waterproofed. In addition a radiator mounted high on the vehicle to prevent off-road damage. It was to be airlifted and air-dropped also, as well as lasting 12 years without revision in the most punishing conditions.
Over 61 companies were declared interested, but only three submitted their completed prototypes: AM General, Chrysler Defense, and Teledyne Continental. AM General prototype was ready in June 1980, and one year later, AM general was awarded the contract for several prototypes for tests, along with the two others, producing 11 prototypes that were tested in a 600,000 miles course including desert and arctic conditions. AM general prototypes were 2400 kg in curb weight, for a 6.2 L (380 cu in) V-8 diesel and a three speed gearbox. AM final production contract was awarded in 1983, for 2,334 vehicles. This was followed by a first batch of 55,000 vehicles to be delivered withing 5 years, and deliveries totaled 100,000 by 1995.
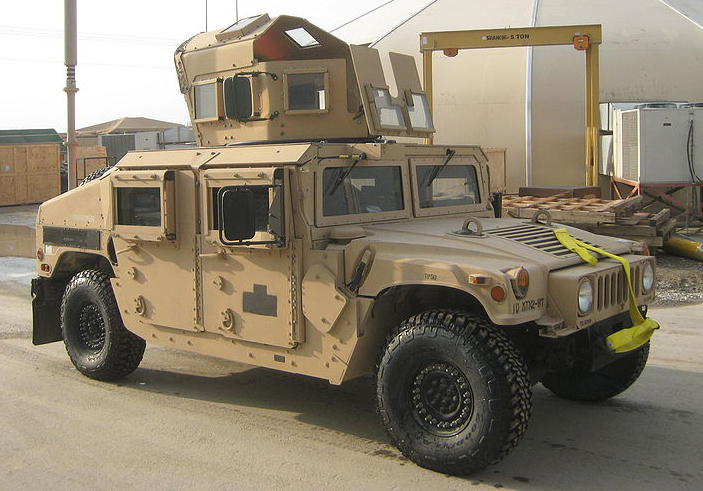

M1151 with add-on armor
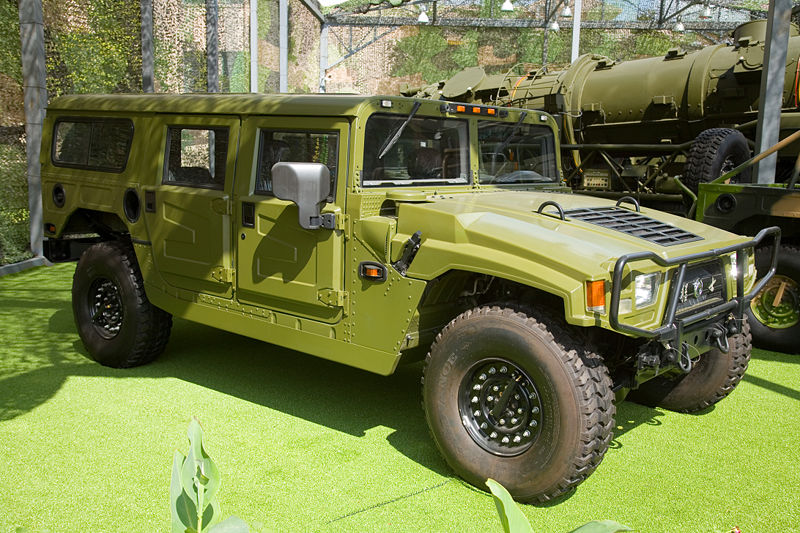
It is resting on a narrow steel frame with boxed rails and five heavy duty cross members for extra rigidity. The chest-high transmission hump separated the crew but allowed the seats to be lowered, keeping the entire vehicle low profile and most components protected high up by a reinforced cage structure. The driver and co-driver had both large vertical windshields with bulletproof glass, as well as two other on the side walls. The roof is rigid, as the monocorps hull structure, providing overhead protection against small arms fire and shrapnel, but provides no collective NBC system. Improvements were added to the bottom, as proven vulnerable to Improvised Explosive Devices (IED) and mines during Operation Afghan Freedom and Operation Iraqi Freedom.
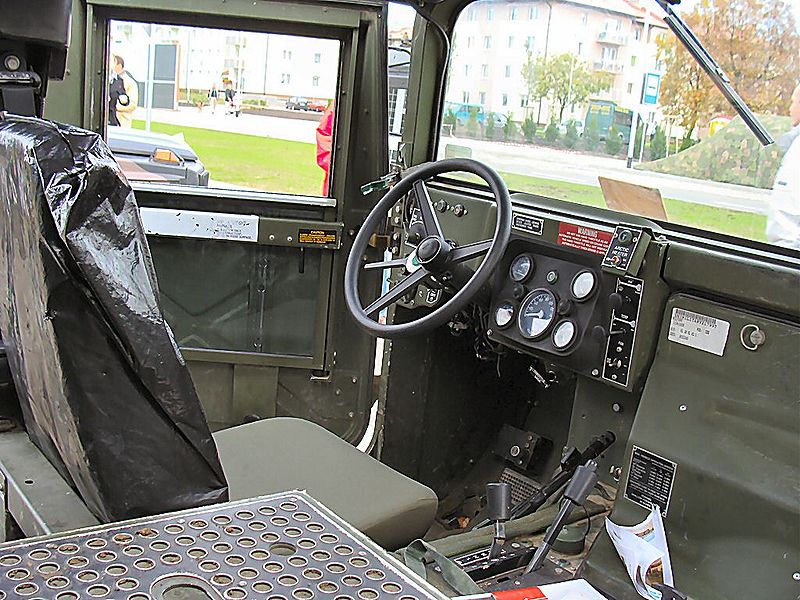

Interior of a Humvee
The standard interior of the Humvee is spacious, with two front seats separated by the massive transmission tunnel, two seats at the rear, and a large rear open storage area, large enough for four more personal or a 1,100 kg payload or a closed compartment with rear doors depending on the versions. Despite this they can be carried by most US transport helicopters and cargo planes. They are sturdy enough, and were tested to endure the Low Altitude Parachute Extraction System (LAPES).

Humvee M1113 with a chassis-mounted XM1124 hybrid Electric diesel
The engine was either the GM V8 diesel 6.2 L (380 cu in) or the V8 turbo diesel 6.5 L (400 cu in), both giving 190 hp (142 kW) @ 3,400 rpm or 380 lbf·ft (515 N·m) at 1,700 rpm, served by a 3-speed automatic or 4-speed automatic. Top speed was 55 mph (90 kph) at max payload, but up to 70 mph (113 kph) with a moderate payload. The average cross-country speed was over 40 mph. On its internal fuel of 25 U.S. gallons (95 L), it could travel up to 400 km. It also have a towing hook for a payload trailer of 9,000 pounds (4,100 tons).

Humvee with a Raytheon SAM
With the experience in Somalia (1993) and Bosnia (1994), better turbo-charged engines was adopted, and following the Afghan and Iraqi war experience, air conditioning became essential as well as extra protection features. The improved Expanded Capability Vehicle 2 (ECV 2) series came in 2008-2009. It was intended to regain mobility despite the increased weight of armor, and the TD engine was improved. As of 2011 an effort was made to try to balance the inventory fleet, both the active and reserve. Indeed, the Army National Guard ended with more HMMWVs than the active units, http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/systems/ground/hmmwv.htm
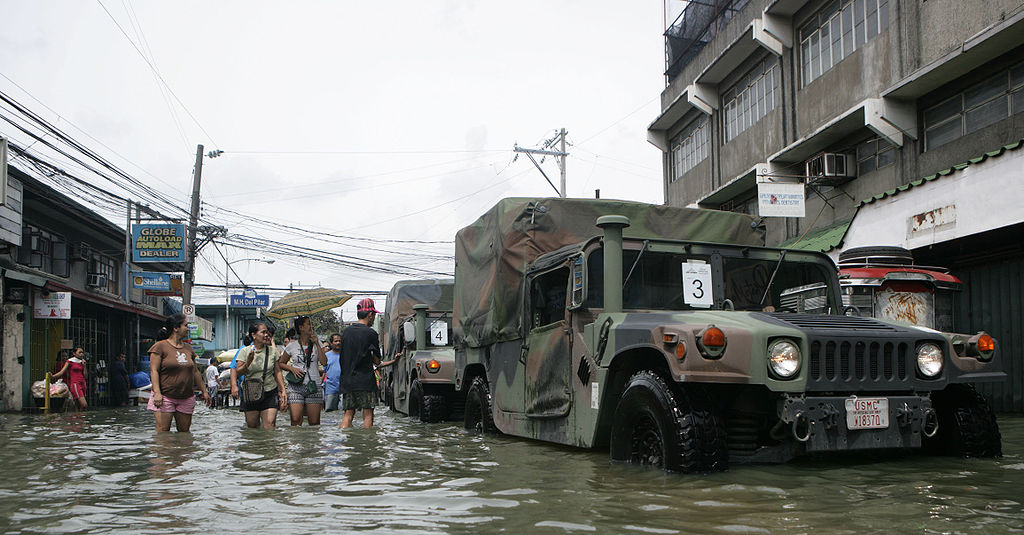
Operation Desert Shield/Storm was the first theater-wide use of the Humvee. It was in the Iraqi desert that the Humvee made its mark and became famous. As the modern Jeep, the Humvee proved to be rugged and dependable. The Humvee handled the open desert easily. It more than kept up with the speed of the first Gulf War. Humvees were used by all parts of the military and were seen regularly on the news. It easily met the requirements of the American military in its various roles. By the end of the month long conflict, the Humvee had cemented itself into the U.S. military as the new tactical workhorse.
However, a decade later, the Humvee would be put back into battle in Afghanistan and Iraq in 2003. As an open terrain, off-road support vehicle, the Humvee performed above expectations. However, as an urban combat vehicle, the Humvee showed its weaknesses. The aluminum body and frame were designed for off-road performance, not for ballistic and explosive protection for soldiers. Although armored doors, windows, and plates gave the soldiers some protection, the overall structural integrity of the Humvee was not improved. Improvised Explosive Devices (IED) and Rocket Propelled Grenades (RPG) became the most effective weapons against the Humvee.
In an urban combat situation, the Humvee also proved to be a sitting duck, easily targeted by insurgents. The Humvee's top speed topped out at over 65 mph. However, when patrolling the streets, it usually kept the pace of the infantry on foot that were clearing buildings. This meant that the Humvee sat in the street, idle, while its infantry detachment cleared a building. Sitting still, they were easy targets for insurgents. Simply, the Humvee was not designed for urban combat. It was designed for off-road use during conventional warfare. Speeding through the desert or climbing mountain passes, the Humvee performed at its best. Unfortunately, it was the only vehicle available for wide-spread operations at the time.
Today, the Humvee is still in service, but it has taken a back seat to the new Joint Light Tactical Vehicle and the MRAP vehicle. The Humvee is still a viable platform for support roles such as ambulances, missile platforms, detection units, light cargo haulers, staff cars, and the like. Overall the Humvee has an excellent battle record in its intended role, and as an AFV. Unfortunately, the United States military tried to use it in an urban combat role, and many soldiers were wounded or killed because of it. The lessons learned from the Humvee have spurred new developments and requirements for the American military in the MRAP and JLTV.
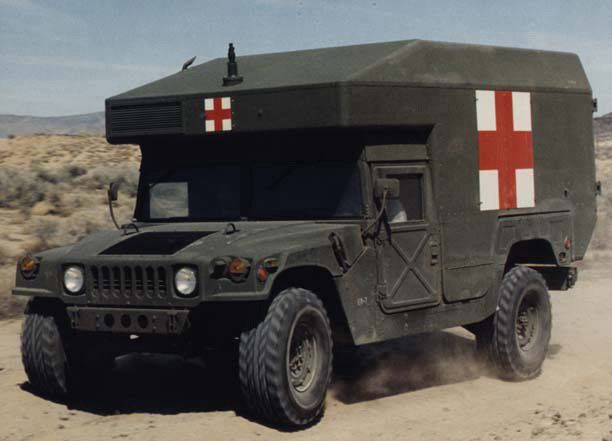

M997 Heavy Ambulance of the USMC
Depending on the climate and temperatures, Hummers of these "open air version" came with a diverse area of soft-top plastic and fabric enclosures.
-M1097 Heavier Cargo Carrier: Same configuration, but reinforced chassis.
In 1991 the Ml097 Heavy Hummer Variant (or HHV) featured an upgraded suspension, drive train, but with the same 15Ohp GM V8 6.2 Liter diesel fuel injected engine. Greater payload and more shelters.
The M1025 is generally similar to the basic M998 HMMWV variant, but with a basic armor, and roof mounting base for a large array of weaponry being mounted. The M1026 receive a basic armor and winch, the M1043 receive with supplemental armor and the M1044 Supplemental Armor and Winch. -M1043/M1044 Troop/armament carrier: 4 doors, open bay for rapid dismounting of troops, distinctive rigid rear.-M1045/M1046 heavier troop/cargo carrier: Same configuration but distinctive "x" rigidity bars on the doors and other details.
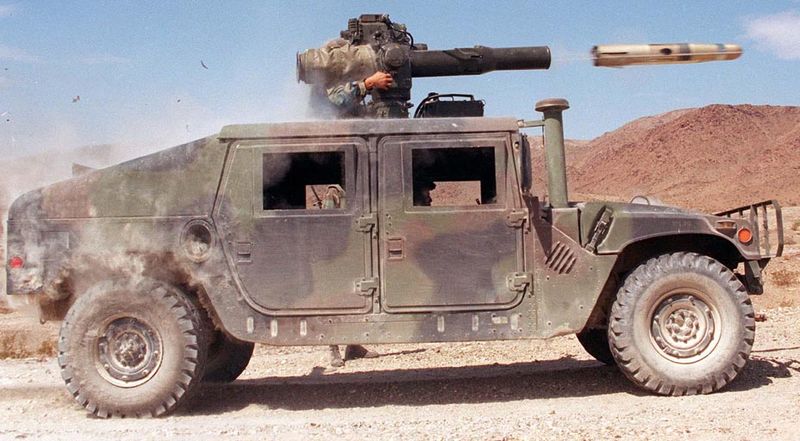

Humvee firing a TOW missile
- Composite Humvee. Regular aluminium hull replace by a new 450 kg cell made by TPI Composites of Rhode Island with AM General.
- XM1124 Hybrid-Electric Humvee, mobility prototype with an all-electric drive train from RDECOM/TARDEC, intended for Spec Ops.
The M1114 is used as a special operations vehicles and communications shelter carrier, chiefly. The sum of improvements is similar to the spec ops Ground Mobility Vehicle, comprising a heavier suspension, more rugged tires, improved ground clearance, a more powerful engine, an open bed for improved storage and access, a towing winch (4,200 pounds cap.) and GPS navigation. Normal cruising range is over 275 miles.

Humvee STAR-T Telecom
Variants includes the M1114/16/23/24/25/65 up-armored carriers, M1115/21/67 TOW and improved TOW up-armored carriers, and the M1151/52 up-armored capable HMMWV which were designed for urban combat.
Humvees in patrol March 2008
Woek In progress !

M1114 with a Kevlar Armour in patrol

Marine Humvee M1123 with Bolt-on Armour
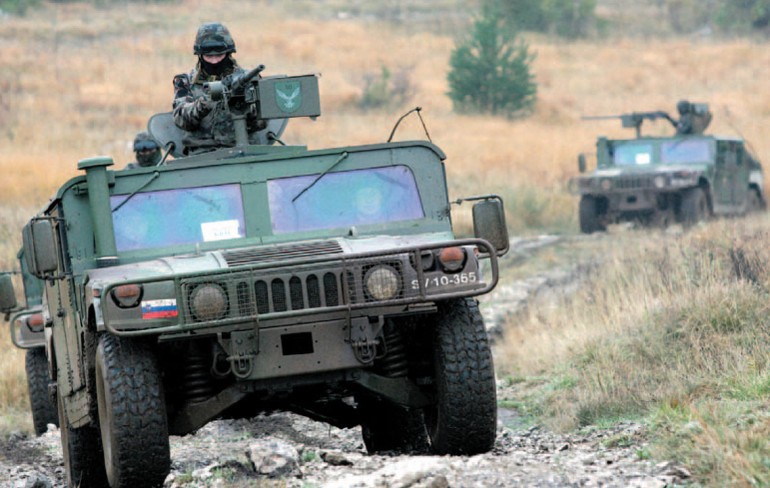

Slovenian Humvees
Major operators are:
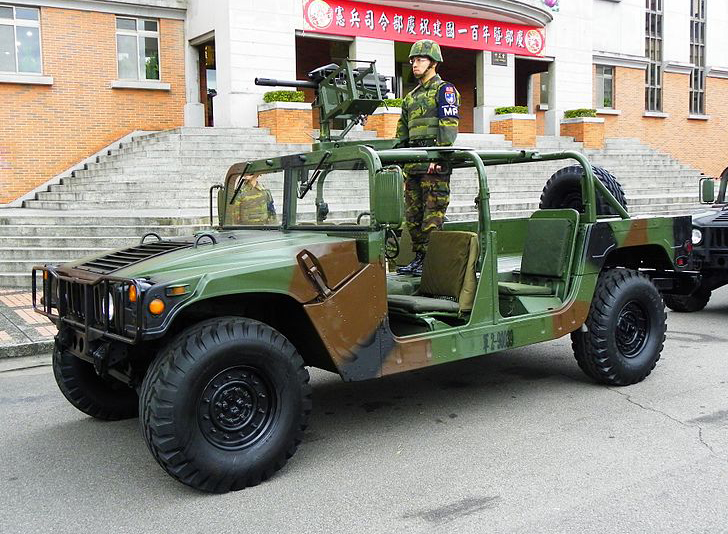 Taiwanese ROC Humvees at the Military Police Headquarters
Taiwanese ROC Humvees at the Military Police Headquarters
Other customers includes: Albania (20), Bahrein (unknown), Bosnia-Herzegovina (a few used for de-mining operations in Iraq), Bolivia: (50 vehicles only for the "Green Devils" anti-narcotic unit and Rangers), Botswana (40), Bulgaria (52), Canada (A few used by y JTF-2 and CSOR in Afghanistan), Chad (Some, Sold through the Foreign Military Sales program), Croatia (85), Czech Republic (601st Special Forces Group), Denmark (30), Djibouti, Dominican Republic, El Salvador (20), Ecuador (130), Ethiopia, Georgia (110+), Honduras, Hungary (27-Afghanistan), Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Jordan (130+), Kenya, Latvia (60), Luxemburg (43), Macedonia (80), Moldova (39), Monaco (6), Mongolia (30), New Zealand, Norway (6), Panama (7), Oman, Peru (34), Portugal (37), Romania (122), Russia (8, seized in Ossetia and evaluated), Saudi Arabia, Serbia (21), Slovakia, Spain (150+, Marines), Sudan, Tanzania, Thailand, Tunisia (52), Ukraine (110), UAE, Uganda (50), Venezuela, Yémen (13).
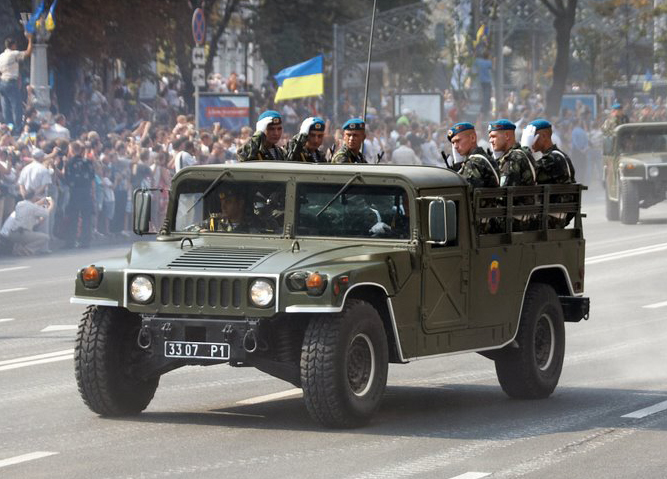 Ukrainian Humvees at the Kiev National parade
Ukrainian Humvees at the Kiev National parade
 Influences: Chinese PLA Dongfeng EQ2050
Influences: Chinese PLA Dongfeng EQ2050
The Humvee model kit blog - hmmvinscale.com
Humvee model kit Forum (Polish)
The Humveeon war-wheels.net
Israeli Hummers (Fr)
AM General Website
Hummer Network
Video: Promotional of the first civilian Hummer, 1980s
HMMMV in scale
NOTE: This post is a placeholder for SEO purpose/ It does not represent the quality and depht of the final article
The Modern Jeep
The High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicles, HMMWV, or Humvee, was designed to replace the aging Jeep in the American military. The Jeep served U.S. troops well over its four decade tenure, but it desperately needed an update. The Humvee would become the modern day Jeep.As Armored Personnel Carriers (APC) go, the M113 was the most produced tracked APC, at 88,000+. However, the most produced armored personal carrier is the Humvee. Unveiled in 1983, 280,000 vehicles have been built so far. It still comes in less than the iconic vehicle it replaced, the Jeep, of which 650,000 were made. The Humvee was produced to be fully enclosed and Nuclear (Radiation), Biological, Chemical (NBC) proof. The Jeep was never considered to be "armored" as it was an open cab vehicle. Conversely, the Humvee, up armored, is considered an armored fighting vehicle.
The utility and versatility of the vehicle was well proven after the end of the Cold War. A familiar sight in the Gulf wars and in Afghanistan, the Humvee was well-known and well-showcased by the world wide media, and became an iconic symbol of these conflicts, just as the Huey helicopter was to Vietnam. This is the quintessential modern U.S. "Battle Taxi", although this was not its primary objective or duty. The Humvee was largely exported and also inspired a wide range of civilian adaptations and applications.

Humvee with a FRAG-6 reinforced add-on armor in April 2010
Replacing and Improving a Legend
When the first studies started in the 1970s, the goal was simple: The Jeep was showing its age, despite modernization allowing this nimble vehicle to remain relatively up-to-date in the Vietnam War. The final Jeep iteration, the quarter-ton M151 Military Utility Tactical Truck or MUTT, had a number of failed innovations. Perhaps the worst was the tendency of the M151 to roll over at low speeds, causing a number of non-combat casualties. The Army also had a heavier truck, the half-ton M561 Gamma Goat, which also needed to be replaced due to a lack of reliability. The Army was not interested in designing two tactical vehicles at this point. They wanted to have one vehicle that could be used in the quarter-ton and half-ton truck roles.The Jeep design had one overarching flaw from its inception in 1939. There was no protection for the passengers. As the Cold War progressed, there was no protection for the Jeep crew in case of an NBC threat or against shrapnel and small arms fire. The original Jeep was open where crew can literally jump in and out. However, during combat (not infrequent as it was used for reconnoitering in enemy territory), the driver had to react quickly and retreat swiftly before the enemy could effectively return fire. A completely armored, encased body would had the advantage of offering this supplementary protection without loosing the "fast descent" characteristic of the older model.
The idea of fitting an open back where soldiers can quickly embark and disembark without bothering with doors or hatches, was perhaps something related to the deeply popular and deeply rooted affection of civilians for pickup trucks. This trade-off with NBC protection was relative as the main 4-seats compartment was still fully enclosed. The Humvee was not a traditional APC due to its size and primary duties of reconnaissance and liaison. However its stiff construction and size allowed to adapt a large variety of weapons that the Jeep could never mount. So when the vehicle was eventually unveiled, it was praised as indeed the only true possible successor of the vehicle created originally by Bantam in 1939.
First appearance of the HMMWV program
Like many large scale military program, the Humvee gets its name from an unspeakable acronym, HMMWV for "High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle", reminiscent of the "General Purpose" of the previous Jeep. Already in the 1960s, knowing well the possible needs of the army for a replacement, several automotive manufacturers proposed various trucks or semi-trucks and utility vehicles with off-road capabilities. Many were tested by the Army was not interested.The Cheetah
The most notable of these private ventures came from the famous Italian car maker than made a fortune selling their super cars to the wealthy throughout the world, Lamborghini. The brand was indeed better known for its classics like the gorgeous Miura and muscular, space-age Countach and surprised everyone in 1977 with the Cheetah. However it did not came out from the blue. Lamborghini actually approached Mobility Technology International (MTI) for a better access to military top brass, which in turn contracted the company for designing such vehicle. The cheetah was a copy by MTI of the former FMC's XR311 prototype of 1970, already rejected by the Military, which led to a legal action of FCM when the Cheetah was showcased at the Geneva Motor Show.The Cheetah was very much in its appearance a progenitor of the Humvee. It was a powerful true 4x4, not with a Lamborghini V12 as some stated but a better suited engine for military specs, the Chrysler 5.9 liter (360 ci) V8. It was waterproofed and rear-mounted, with a 3-speed gearbox. The reinforced fiberglass prototype was built at MTI in San Jose, California and then sent to Sant'Agata near Bologna where it was completed by Lamborghini. At more than 2 tons (4,502 lb) and with a rear engine, top speed was not the primary objective. The prototype was only showed once unofficially, and stored as AM General was later awarded the contract for a very similar vehicle. Lamborghini however tried later the LM002 of its own design, which never got passed the prototype stage and did not profit the already dwindling finances of the company following the first petrol crisis in the 1970s.
AM General prototype
AM General (South Bend, Indiana) was not a known car maker but a heavy duty vehicle manufacturer, accustomed mostly to buses and trucks, but also Jeeps. The former company Standard Wheel Company expanded to off-road vehicles when absorbing Overland Automotive before the war, which became Willys-Overland, maker of the original jeep. After World War II, it was absorbed by Kaiser Motors, and itself became the Kaiser-Jeep Corporation in 1963. Then absorbed by American Motors and renamed AM General. It was a natural choice for making the next generation of US Jeep as the company linage did. Kaiser earned US$87 million Army truck contract in 1964, that really came to fruition in 1979, when the definitive program was launched.The final specifications for a High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle were drafted in 1979, originally to replace the 1/4 to 1 1/4-ton range M151 MUTT and M565 Gamma Goat. Paramount was the off-road performance, but also a large payload capacity and extensive armor protection against indirect fire. Another demand for the width was to fit inside standard cargo planes as well as European tunnels, bridges, and roadways. At the end it was far larger than the jeep and twice as heavy, with improved suspensions and a 410 mm ground clearance. Field performances expected were climbing a 60% slope or stay stable on a 40% slope, ford 5 ft (1.5 m) of water unprepared thanks to a snorkel air intake and electronics waterproofed. In addition a radiator mounted high on the vehicle to prevent off-road damage. It was to be airlifted and air-dropped also, as well as lasting 12 years without revision in the most punishing conditions.
Over 61 companies were declared interested, but only three submitted their completed prototypes: AM General, Chrysler Defense, and Teledyne Continental. AM General prototype was ready in June 1980, and one year later, AM general was awarded the contract for several prototypes for tests, along with the two others, producing 11 prototypes that were tested in a 600,000 miles course including desert and arctic conditions. AM general prototypes were 2400 kg in curb weight, for a 6.2 L (380 cu in) V-8 diesel and a three speed gearbox. AM final production contract was awarded in 1983, for 2,334 vehicles. This was followed by a first batch of 55,000 vehicles to be delivered withing 5 years, and deliveries totaled 100,000 by 1995.
Design
Protection
The Humvee look is unmistakable, with only the vertical radiator grooves of the original jeep still showing on the hood, but the rest is unique. The Humvee is very wide at 7 feet (2.16 m), giving it stability on all terrains. It is also low in height at 6 feet (1.80 m), making it a difficult target to spot and hit, but was only a benefit of the specification about stability. Former Jeeps had tendencies to top over. The hull is made of rust-free, high-resistance heat-treated aluminum alloy.
M1151 with add-on armor
It is resting on a narrow steel frame with boxed rails and five heavy duty cross members for extra rigidity. The chest-high transmission hump separated the crew but allowed the seats to be lowered, keeping the entire vehicle low profile and most components protected high up by a reinforced cage structure. The driver and co-driver had both large vertical windshields with bulletproof glass, as well as two other on the side walls. The roof is rigid, as the monocorps hull structure, providing overhead protection against small arms fire and shrapnel, but provides no collective NBC system. Improvements were added to the bottom, as proven vulnerable to Improvised Explosive Devices (IED) and mines during Operation Afghan Freedom and Operation Iraqi Freedom.

Interior of a Humvee
Mobility
An all wheel drive was essential to the Humvee design, and an ingenious independent double-wishbone suspension units with heavy duty and helical gear-reduction hubs were installed for better ground clearance. There were disc brakes mounted high-up on all wheels outside of each differential (front-rear torsion, center locker type). The biased differentials allows forward motion as long there is one wheel in contact has traction. There is also an electronic traction system that engages when the vehicle is about to top over. Tires are 37 x 12.5 radial tires with run-flat cells. In addition there is an optional centralized tires inflation system (central tire inflation system or CTIS which was introduced on the DUKWs during World War II) helping to optimize ground pressure and contact surface performances on all terrains.The standard interior of the Humvee is spacious, with two front seats separated by the massive transmission tunnel, two seats at the rear, and a large rear open storage area, large enough for four more personal or a 1,100 kg payload or a closed compartment with rear doors depending on the versions. Despite this they can be carried by most US transport helicopters and cargo planes. They are sturdy enough, and were tested to endure the Low Altitude Parachute Extraction System (LAPES).

Humvee M1113 with a chassis-mounted XM1124 hybrid Electric diesel
The engine was either the GM V8 diesel 6.2 L (380 cu in) or the V8 turbo diesel 6.5 L (400 cu in), both giving 190 hp (142 kW) @ 3,400 rpm or 380 lbf·ft (515 N·m) at 1,700 rpm, served by a 3-speed automatic or 4-speed automatic. Top speed was 55 mph (90 kph) at max payload, but up to 70 mph (113 kph) with a moderate payload. The average cross-country speed was over 40 mph. On its internal fuel of 25 U.S. gallons (95 L), it could travel up to 400 km. It also have a towing hook for a payload trailer of 9,000 pounds (4,100 tons).
Armament
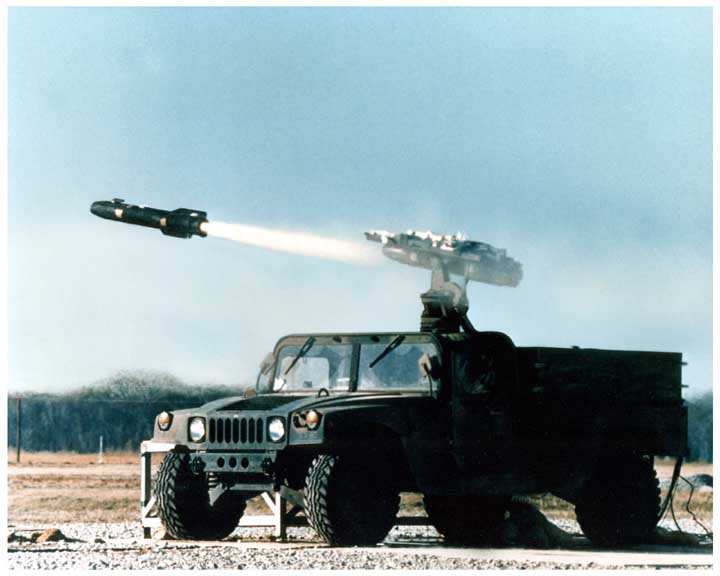
There are 17 major variants of the Humvee, and many sub-variants with many weapons systems. Although the basic "battle taxi" is equipped with a central ring-mount for the "Ma Deuce" cal.50 M2HB heavy machine gun, the Hummer could be modified for numerous platforms including TOW and Stinger missiles, as mortar carrier, the M134 Minigun, Mk 19 grenade launcher, M240G/B machine gun and M249 LMG.
Humvee with a Raytheon SAM
Production
In 1983 AM general and its sub-contractors was given a $1.2 billion contract to produce 55,000 vehicles over a 5-year period, later expanded to 1.6 billion for 70,000. Financially AM general stocks were passed to LTV Aerospace and Defense Company on 24 July 1983 and is now its fully-owned subsidiary. Although the basic vehicle was ready this year, it was not until 1984 that other prototypes resumed testing with the first production vehicles reaching the military in March 1985. Additional contracts were obtained in 1989 and 1994. The A1 version was started in 1989, featuring technological, environmental, operational, and safety improvements. The A2 series was started in 1994, also called Expanded Capability Vehicle (ECV) series.With the experience in Somalia (1993) and Bosnia (1994), better turbo-charged engines was adopted, and following the Afghan and Iraqi war experience, air conditioning became essential as well as extra protection features. The improved Expanded Capability Vehicle 2 (ECV 2) series came in 2008-2009. It was intended to regain mobility despite the increased weight of armor, and the TD engine was improved. As of 2011 an effort was made to try to balance the inventory fleet, both the active and reserve. Indeed, the Army National Guard ended with more HMMWVs than the active units, http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/systems/ground/hmmwv.htm
The Humvee in action
When first introduced in 1983, the Humvee replaced the M151 Jeeps (1/4-ton), M274 Mule (1/2-ton), M561 Gamma Goat (1 1/4-ton), and M718A1 ambulance (based on M151 1/4 ton truck), and M792 ambulance (based on M561 1 1/4 ton truck). There were 73,000 Humvees in service by the 1991 Gulf War. Among the earliest in service went to Ft. Lewis, Washington and the 9th Infantry Division. They were used to test the new concept of the motorized division. The Yakima Training Center (Washington) was the main testing ground for HMMWVs from 1985 through December 1991. Reports concluded negatively to the concept, which was abandoned and the unit disbanded.Operation Desert Shield/Storm was the first theater-wide use of the Humvee. It was in the Iraqi desert that the Humvee made its mark and became famous. As the modern Jeep, the Humvee proved to be rugged and dependable. The Humvee handled the open desert easily. It more than kept up with the speed of the first Gulf War. Humvees were used by all parts of the military and were seen regularly on the news. It easily met the requirements of the American military in its various roles. By the end of the month long conflict, the Humvee had cemented itself into the U.S. military as the new tactical workhorse.
However, a decade later, the Humvee would be put back into battle in Afghanistan and Iraq in 2003. As an open terrain, off-road support vehicle, the Humvee performed above expectations. However, as an urban combat vehicle, the Humvee showed its weaknesses. The aluminum body and frame were designed for off-road performance, not for ballistic and explosive protection for soldiers. Although armored doors, windows, and plates gave the soldiers some protection, the overall structural integrity of the Humvee was not improved. Improvised Explosive Devices (IED) and Rocket Propelled Grenades (RPG) became the most effective weapons against the Humvee.
In an urban combat situation, the Humvee also proved to be a sitting duck, easily targeted by insurgents. The Humvee's top speed topped out at over 65 mph. However, when patrolling the streets, it usually kept the pace of the infantry on foot that were clearing buildings. This meant that the Humvee sat in the street, idle, while its infantry detachment cleared a building. Sitting still, they were easy targets for insurgents. Simply, the Humvee was not designed for urban combat. It was designed for off-road use during conventional warfare. Speeding through the desert or climbing mountain passes, the Humvee performed at its best. Unfortunately, it was the only vehicle available for wide-spread operations at the time.
Today, the Humvee is still in service, but it has taken a back seat to the new Joint Light Tactical Vehicle and the MRAP vehicle. The Humvee is still a viable platform for support roles such as ambulances, missile platforms, detection units, light cargo haulers, staff cars, and the like. Overall the Humvee has an excellent battle record in its intended role, and as an AFV. Unfortunately, the United States military tried to use it in an urban combat role, and many soldiers were wounded or killed because of it. The lessons learned from the Humvee have spurred new developments and requirements for the American military in the MRAP and JLTV.
The future
The replacement of the Humvee fleet appeared obvious with the rising losses due to IEDs and mines. This forced the DoD to develop another kind of vehicle. The HMMWV was created to meet the requirements of the potential Cold War, and to to engage the enemy on the large open Eastern European plains in a conventional war. As unconventional warfare progressed for the American military, new solutions were needed, and South African expertise was also requested. Apart foreign vehicles, the DoD mandated private companies to develop a domestic fleet of MRAPs, contracts that eventually conducted Oshkosh to provide a credible replacement for the Hummer, tailored for this kind of warfare. Nevertheless despite its age, and successive modernization campaigns, the Humvee will remain in the US arsenal for years to come, at least in the perspective of a conventional conflict, possibly as long as the original Jeep and more through the civilian market.The civilian Hummer: A wolf in sheep's clothes
The Humvee was marketed as a civilian vehicle by AM General in 1992, as a standalone brand. Its first famous customer was Arnold Schwarzenegger. The first "Hummers" were directly taken off the regular military manufacturing line and were refined for civilian use. Acoustic insulation, more comfortable seats, internal garments and fixtures, and a comprehensive Hi-Fi sound system were but a few of the installed luxuries. Later on, the original model was re-branded as the H1, while the cheaper and more "civilized" H2 and H3 were revealed in turn. However, in December 2014 the DoD began to release 4,000 surplus vehicles to the civilian market (with the gradual introduction of MRAPs), and although used mostly by domestic law enforcement agencies, M998, M998A1, M1038, and M1038A1 were sold with bids starting at $10,000 for off-road use only, still with their original military gear (no modifications).Humvee Iterations
Humvee A1 (1994)
In early 1994, AM General launched production of the A1 series (beginning with the M998). It was later standardized on all US Hummers in service and were incorporated into the M1097 Heavy Hummer Variant (HHV). It integrates upgraded components, new front seats, improved parking brake lever with safety release, metal hood grille, improved slave receptacle, solid state glow plug controller, modified rifle mounts, and upgraded rear half shafts. Standardization was widespread and still ongoing even when came the next A2 upgrade next year.Humvee A2 (1995)
Already when the A1 was only beginning to be the next standard, AM general worked on a better version, which was the M998A2. It was using the M1097A1 HHV as a base and incorporated a 6.5 liter naturally aspirated diesel engine which developed 160hp coupled to a new electronically controlled four-speed automatic transmission. Together with a better output, it came in accordance to the redesigned emissions system meeting all of the 1995 US Government standards. This also came with an increased cargo capacity, better heating system, new rear seats (A1 standard) and self-canceling turn. This upgrade was standardized later, up to 2007.
M997 Heavy Ambulance of the USMC
Variants
The early base vehicle is the M1025 HMMWV (A1 chassis) replaced later by the A2 chassis known as the M1113. Along with the development of nearly twenty base variants (see later) generic options includes a winch with 6,000 lb (2,700 kg) capacity, and add-on armor, or several mounts for the weapons. This list includes the M56 Coyote Smoke Generator Carrier, M707 Knight HMMWV, M966 and M1036 HMMWV TOW M1045/46 up-armored tank hunters, M996/997 hard-top Ambulance and M1035 Soft-Top Ambulance, M998 and M1038 Cargo/Troop carrier, M998 HMMWV Avenger and M1097 Heavy Avenger (Stinger) SPAAMLs, M1025/1026, M1043/44 and M1109 up-armored Armament Carrier, M1037 and M1042 S-250/S-788 Shelter Carriers, M1069 Tractor for the M119 105-mm Gun, the Active Denial System ( directed-energy weapon), Ground Mobility Vehicle (special ops variant), IMETS (Integrated Meteorological System) and ZEUS-HLONS (Laser Ordnance Neutralization System) to neutralize explosive ordnance.- M707 HMMWV Striker
- M966 HMMWV TOW Armored
- M996 Mini-Ambulance, Armored
- M997 Maxi-Ambulance, Armored
- M998 Cargo/Troop
- M998 HMMWV Avenger
- M1025 Armament Carrier, Armored
- M1026 Armament Carrier, Armored W/W
- M1035 Soft-Top Ambulance
- M1036 TOW Armored W/W
- M1037 S-250 Shelter Carrier
- M1038 Cargo/Troop Carrier W/W
- M1042 S-250 Shelter Carrier W/W
- M1043 Armament Carrier, Up-Armored
- M1044 Armament Carrier, Up-Armored W/W
- M1045 TOW Up-Armored Armor
- M1046 TOW Up-Armored Armor W/W
- M1069 Tractor for M119 105-mm Gun
- M1097 Heavy HMMWV Avenger
- M1109 Up-Armored Armament Carrier
- M1113 Expanded Capacity
- M1114 Up-Armored Armament Carrier
- M1116 Up-Armored HMMWV
- M1123 Heavy Humvee carrier
- M1121 TOW Armored
- M1145 Up-Armored HMMWV
Evolution
As shown in the graphic above, the basic 1983 Hummer was already divided into six main versions and more than 20 sub-types. The basic versions included an Armament Carrier, TOW Missile Carrier, Ambulance Carrier, Shelter Carrier and a Prime Mover. The Prime Mover was designated M998, the Armament Carrier M1025. The Prime Mover was capable of towing the M119 light howitzer or M167 VADS system. The Shelter Carrier was also designed a heavy cargo capable of handling payloads up to 4,400 pounds (M1037).Basic cargo/troop carrier:
-M998 and M1038 Basic Cargo Carrier: No roof, no side doors (or soft ones), rigidity bar and rear open bay with benches The Cargo/Troop Carrier and its numerous derivatives were developed right at the beginning.Depending on the climate and temperatures, Hummers of these "open air version" came with a diverse area of soft-top plastic and fabric enclosures.
-M1097 Heavier Cargo Carrier: Same configuration, but reinforced chassis.
In 1991 the Ml097 Heavy Hummer Variant (or HHV) featured an upgraded suspension, drive train, but with the same 15Ohp GM V8 6.2 Liter diesel fuel injected engine. Greater payload and more shelters.
Specialized cargo carrier:
-M1037/1042 Specialized Cargo Carriers: Rear doors and rigid cargo bay at the rear. This version came out in 1995 as the Expanded Capacity Vehicle (ECV) or up-Armored XM 1109 with no loss in cargo-carrying ability and a payload which rises from 4,400lb to 5,300lb payload compared to the M1097A2. It was given a 6.5L turbo diesel engine generating 19Ohp to cope with the supplementary weight. Uses also the AM General's Cap-Over Hummer Variant (COHHV) cargo truck components. These consists in a reinforced frame, modified differentials and steering system, improved half shafts, exhaust system, brakes, cooling system, suspension, and wheels. Starting in 1995, Central tire inflation systems and an air conditioning units were made standard.Specialized troop/armament carriers (M1025)
Introduced in 1983, this version can be summarized as the "fully enclosed hummer". In fact its most distinctive aspect was the rear sloped tail over the cargo bay, which could carry cargo and troops in "descent" mode. This was the basic APC in widespread use by the US Military in the 1986 Panama operation, 1991 Gulf War, OAF, and OIF. The fully enclosed interior guaranteed collective NBC system and extra rigidity to mount a large variety of light to heavy armament; The basic version came with a 12.7 mm M2HB "Ma Deuce" HMG (cal .50). In fact the array comprised also the M249 5.56mm SAW, M60 and M240 7.62mm MGs, M60 7.62mm MG, MK 19 Mod 3 40mm Grenade Launcher. In the early 2010s, RWS systems became commonplace, especially in Iraq.The M1025 is generally similar to the basic M998 HMMWV variant, but with a basic armor, and roof mounting base for a large array of weaponry being mounted. The M1026 receive a basic armor and winch, the M1043 receive with supplemental armor and the M1044 Supplemental Armor and Winch. -M1043/M1044 Troop/armament carrier: 4 doors, open bay for rapid dismounting of troops, distinctive rigid rear.-M1045/M1046 heavier troop/cargo carrier: Same configuration but distinctive "x" rigidity bars on the doors and other details.
Ambulances:
M1035 Mini Armored Ambulance:: Rear compartment modified for 2 stretchers. It was derived into the M1035A2 in 1998 and a new version M???? in 2007. M997 Maxi Armored Ambulance: Brand new rigid compartment large enough for 4 stretchers, 8 ambulatory and medics. Equipped with air conditioning and later declined into A1 and A2. Cold air could be equipped with the Gas-Particulate Filter Unit (GPFU) in an NBC environment. The latter system also provides regulation for the crew protective masks or M13 series patient protective masks. Field performances are kept high with a 60%(31°) climbing capability, 40% (22°) side slope, and ford up to 1,52m (60 in) with the kit. The next version A1 only was standardized to the generic A1 standard, but the A2 received new bumpers and structure reinforcements. A self-recovery winch also came as an option. From 2003 on, it also came with various add-on armor packages (P1 and following). The TBD version was added to the lineage in 2009.
Humvee firing a TOW missile
Prototypes
- Scorpion, a regular 2004 heavy chassis modified to carry the 2B9 Vasilek 82 mm automatic mortar.- Composite Humvee. Regular aluminium hull replace by a new 450 kg cell made by TPI Composites of Rhode Island with AM General.
- XM1124 Hybrid-Electric Humvee, mobility prototype with an all-electric drive train from RDECOM/TARDEC, intended for Spec Ops.
The Expended Capacity Vehicle (ECV)
In 2004 was introduced the new M1114 for the Army and Marines, also known as the "up-armored Humvee" and ECV. It is the sum of experience gained in both OPERATION DESERT STORM and OIF that incorporates some extra protection for urban combat and IED/mines, although its low center of gravity and flat belly made it a poor MRAP/MPV and is globally enhanced in any direction. The first ECV for Expanded Capacity Vehicle was developed in 1995 and had a 6.5 liter Turbo diesel engine generating 19Ohp along with up-armored panels and extra rigidity features.The M1114 is used as a special operations vehicles and communications shelter carrier, chiefly. The sum of improvements is similar to the spec ops Ground Mobility Vehicle, comprising a heavier suspension, more rugged tires, improved ground clearance, a more powerful engine, an open bed for improved storage and access, a towing winch (4,200 pounds cap.) and GPS navigation. Normal cruising range is over 275 miles.

Humvee STAR-T Telecom
Variants includes the M1114/16/23/24/25/65 up-armored carriers, M1115/21/67 TOW and improved TOW up-armored carriers, and the M1151/52 up-armored capable HMMWV which were designed for urban combat.
The Humvee in combat

Humvees in patrol March 2008
Woek In progress !

M1114 with a Kevlar Armour in patrol

Marine Humvee M1123 with Bolt-on Armour
Post-Irak invasion and Afghanistan Modifications
This chapter is about the lessons learned with the Hummer after the Iraq invasion in 2002 and the long war of 2003-2018, when the last US troops left the Iraqi soil, while policing in Afghanistan is an ongoin process.Operators:
The USA now still operates without real replacement the Hummer and its versions and improvised versions, perhaps 150,000 in all (Formerly in total Army: 260,000, Marine Corps: 44,000), including some 1980s vehicles that had been completely overhauled. They are also in service with 71 countries.
Slovenian Humvees
Major operators are:
- - Afghanistan: Operates some 4150 vehicle ordered and delivered from 2010.
- - Algeria: More than 400 ordered.
- - Argentina: About 300 vehicles for the Army, Gendarmeria and IMARA.
- - Chile: 250 army and 50 navy.
- - Colombia: 400+ vehicles
- - Egypt: 3,890+ vehicles
- - Greece (600+ license-built by ELBO).
- - Iraq (New Iraqi Army and security Forces: 10,000+ Humvees)
- - Israel (2000+ assembled by AIL)
- - ISIS (Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant), some 2,300 captured (est.)
- - Lebanon (1300+)
- - Libya (200, donated 2013)
- - Lithuania (200)
- - Mexico (3000)
- - Morocco (3500+)
- - Philippines (300)
- - Taiwan (7000+)
 Taiwanese ROC Humvees at the Military Police Headquarters
Taiwanese ROC Humvees at the Military Police HeadquartersOther customers includes: Albania (20), Bahrein (unknown), Bosnia-Herzegovina (a few used for de-mining operations in Iraq), Bolivia: (50 vehicles only for the "Green Devils" anti-narcotic unit and Rangers), Botswana (40), Bulgaria (52), Canada (A few used by y JTF-2 and CSOR in Afghanistan), Chad (Some, Sold through the Foreign Military Sales program), Croatia (85), Czech Republic (601st Special Forces Group), Denmark (30), Djibouti, Dominican Republic, El Salvador (20), Ecuador (130), Ethiopia, Georgia (110+), Honduras, Hungary (27-Afghanistan), Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Jordan (130+), Kenya, Latvia (60), Luxemburg (43), Macedonia (80), Moldova (39), Monaco (6), Mongolia (30), New Zealand, Norway (6), Panama (7), Oman, Peru (34), Portugal (37), Romania (122), Russia (8, seized in Ossetia and evaluated), Saudi Arabia, Serbia (21), Slovakia, Spain (150+, Marines), Sudan, Tanzania, Thailand, Tunisia (52), Ukraine (110), UAE, Uganda (50), Venezuela, Yémen (13).
 Ukrainian Humvees at the Kiev National parade
Ukrainian Humvees at the Kiev National parade
The Foreign military Sales program
Many of the aforementioned countries were supplied with Humvees according to a dedicated facilitation framework by the DoD for the sales of defense equipment, services, and military training. The Defense Security Cooperation Agency was charged of the supply of vehicles locally and training as the Defense Contract Management Agency. Apart Humvees, F16 fighters were also procured that way to many governments. Influences: Chinese PLA Dongfeng EQ2050
Influences: Chinese PLA Dongfeng EQ2050
Influences:
With such numbers and media presence in the Gulf war, Iraq and Afghanistan, the Humvee looked like the superstar of its category and influenced many foreign models. Cheaper and easier to produce than main battle tanks, it gave many countries the impetus to develop their first local Utility Vehicle. Influences can been seen through the Brazilian Agrale Marruá, Polish AMZ Tur, Ukrainian Dozor-B, Russian GAZ-2975 "Tigr", Chinese EQ2050, Philippine MMPV, Mowag Eagle, Otokar Cobra, Pindad Komodo, Renault Sherpa, URO Vamtac...The future: Is the Humvee obsolete ?
In the years 2005-2012 a flurry of new vehicles started to replace the Hummers on the hottest sites for patrols, and it coincided with the apparition of private companies. The goal was to replace gradually the Hummers that were badly hit by IED, RPG and mine explosions. The designated vehicle to replace it was known in generalHumvee links & resources
The Humvee on WikipediaThe Humvee model kit blog - hmmvinscale.com
Humvee model kit Forum (Polish)
The Humveeon war-wheels.net
Israeli Hummers (Fr)
AM General Website
Hummer Network
Video: Promotional of the first civilian Hummer, 1980s
HMMMV in scale
Humvee specifications | |
| Dimensions (L-w-H) | 8.43 x 3.51 x 3.18 m (331 in x 138 in x 125 in) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 3,810 kg (84,00 lbs) |
| Crew | 2+4 (Commander, Driver, 4 infantry) |
| Propulsion | V8, 6.2-liter fuel injected diesel, 150 hp @ 3,600 rpm |
| Transmission | automatic with maximum input torque of 451 lb/ft. (612N-m) |
| Maximum speed | 65+ mph (48 km/h) on road |
| Suspension | Torsion bars |
| Range (Fuel) | (cc Liters/ cc.) |
| Armament | Standard cal.50 M2 (12.7 mm) -see notes |
| Armor | HT aluminium 8 mm - see notes |
| 280,000 | |
Models and variants

Humvee open top
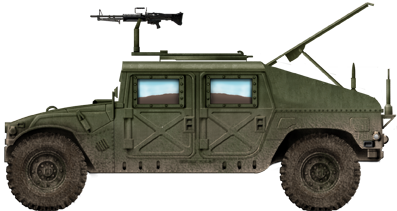
Humvee H1 M1025
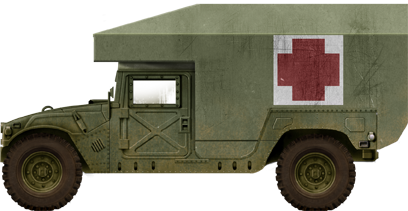
M997A2 Humvee

Humvee M1045 HOT

Military Police in Iraq

M998 Cargo in the gulf war

Humvee T75 - 20mm autocannon RWS
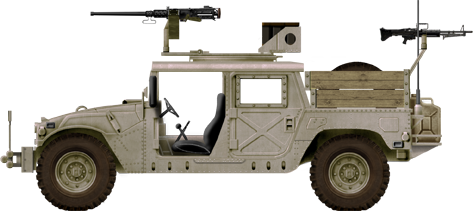
M1025 Humvee, Iraq war 1991.
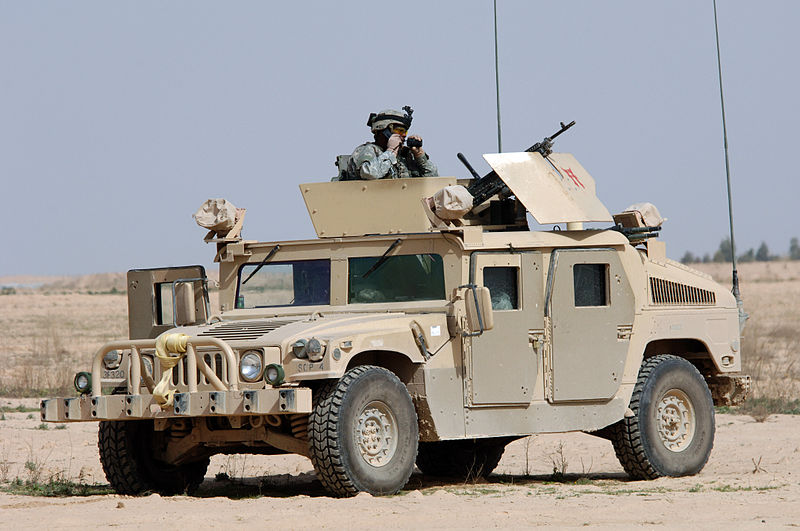

Humvees in patrol with Iraqi soldiers, Bravo Battery 3rd Battalion 320th Field Regiment Saladin Province Iraq March 2006










Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army
Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

