It was clear that well before intending any amphibious operations, a specialized vehicle would be useful to carry troops and supplis from shore to shore. The Heereswaffenamt in 1935 was seeking a way in particular for Wehrmacht engineers (pioneers) to have such vehicle, called "Landwasserschlepper" (abbreviated in LWS) as a lightweight river tug capable of operating on land with good carrying capacity. It was mostly a riverine vehicle, able to provide the genie river crossing and bridging capabilities. Eventually, Rheinmetall-Borsig of Düsseldorf was retained for the design of a prototype. The company created essentially a motor launch hull mixed with a tracked boat as it had been given twin rear-mounted tunnelled propellers and twin rudders aft. When on land, it travelled on steel-shod tracks with four bogies per side. However the project dragged on in 1939 due to other priorities, but was relaunched after France fell, as it would be have used in Operation Sealion, the invasion of Great Britain through the channel.
Therefore the company sped up the process and eventually by the autumn of 1940 had develivered three prototypes. They were immediately assigned to Tank Detachment 100 to take part of Operation Sea Lion as planned. The idea was they would pull ashore unpowered assault barges during the crossing, and tow vehicles across the beaches to avoid them to be bogged down in sand. Afterwards, the LWS would have been used to carry supplies ashore during the critical six hours of falling tide during which all barges were grounded and unable to move. Towing a Kässbohrer amphibious trailer was part of the design. The latter was capable of transporting 10-20 tons of freight and the LWS had some capacity too. This was nitably to overcome the lack of storage and loading/unloading access of the LWS.
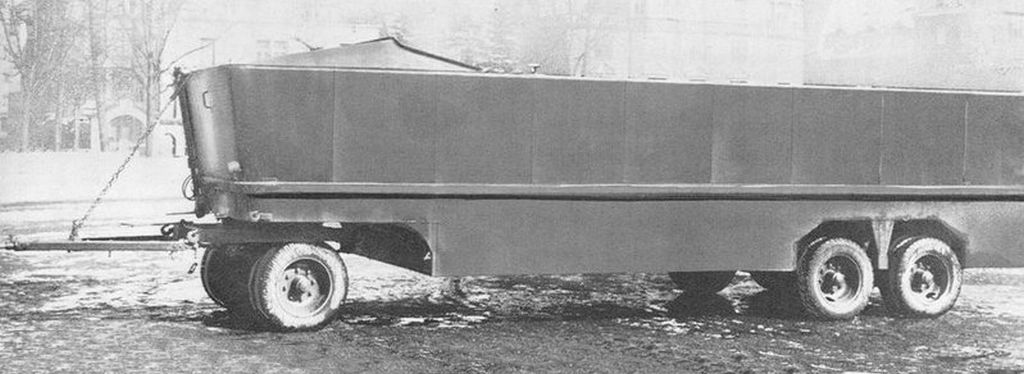
The Kässbohrer amphibious trailer with its wheeltrain. Notice the boat-like front face.
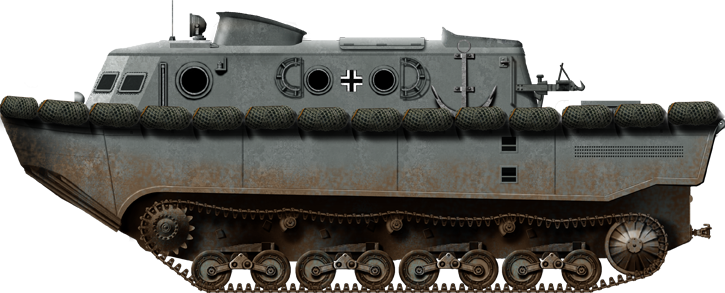
Development went on from 1936 to 1939 with the first 7 vehicles completed in July 1940 and 14 more by March 1941. In addition to 3 men seated in tandem at the front and crew 20 passengers could take place at the back in the gallery. The vehicle however was certainly a heavy prey on land: Massive, unarmored and ponderous, it was a heavy prey in any combat area. Late prodction vehicles differed by having new suspension springs and four return rollers, with Drive sprocket like the Panzer IV. The early version had leaf springs recalling the Panzer II, and three return rollers. The LWS was propelled at sea by a Maybach HL120 V12 engine petrol with a 11,867 cc (724in3) capacity; rated for a 300 hp (224 kW) output at 3,000 rpm, procuring a Power/weight ratio of 8.8 hp/t. There was an observation sea in a tower behind the crew's compartment, with possibly a ring-mounted MG.34, although no photos shows it. It was surrounded by a wavebreaker kiosk and therefore most probably used for guidance at sea in heavy weather as the lower compartment was probably blinded by spray. The vehicle was unarmed, but those carried by the infantry, which could be deployed on the deck. The central compartment was like a bathtub with the boat hull built around to procure buoyancy, so usuful espace was lost there. Just like a boat, the vehicle could be given naval accessories such as buoys, anchors, rubber dingy, rim padding, and steel cable.
It all boiled down to a demonstrated to General Franz Halder, on 2 August 1940. It was organized by the Reinhardt Trials Staff on the island of Sylt (an island in northern Germany, Nordfriesland, Schleswig-Holstein). The general was impressed by the general concept but critical about the tall silhouette on land. He concluded the overall usefulness was clear and proposed to push forward to the OKW that enough LWSs would be available, basically one for two invasion barges. However it was a difficult vehicle to mass-produce, and by the time Rheinmetall-Borsig had devlivered enough of them, Sealion has been postponed. This protracted development could have led to the cancellation of the Landwasserschlepper, but it nevertheless entered service in 1942 and was deployed both in Russia and North Africa in small numbers. By 1944 a new design was created, called the LWS II. It was based on the Panzer IV chassis, featuring a small raised armored driver's cabin and flat rear deck. The engine was fed in air by four fold-down intakes and expussed combustion gasses through exhaust stacks. It was never authorized as there were more pressing issues, and priority was given to tank hunters by that point. Nevertheless, the Landwasserschlepper stayed operational until the end of the war.
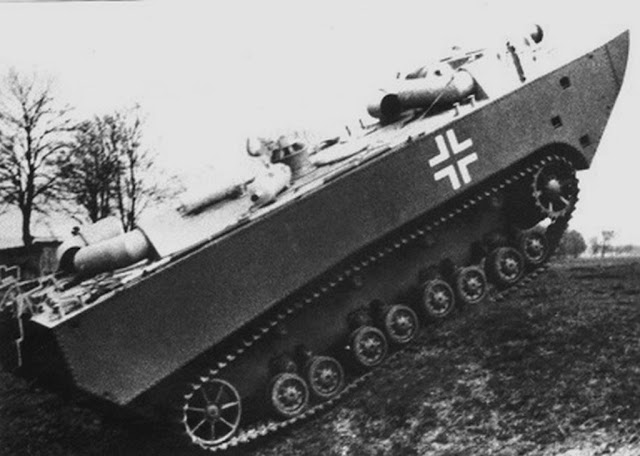

Landwasserschlepper LWS-II

An LWS I in North Africa, 1942
Therefore the company sped up the process and eventually by the autumn of 1940 had develivered three prototypes. They were immediately assigned to Tank Detachment 100 to take part of Operation Sea Lion as planned. The idea was they would pull ashore unpowered assault barges during the crossing, and tow vehicles across the beaches to avoid them to be bogged down in sand. Afterwards, the LWS would have been used to carry supplies ashore during the critical six hours of falling tide during which all barges were grounded and unable to move. Towing a Kässbohrer amphibious trailer was part of the design. The latter was capable of transporting 10-20 tons of freight and the LWS had some capacity too. This was nitably to overcome the lack of storage and loading/unloading access of the LWS.

The Kässbohrer amphibious trailer with its wheeltrain. Notice the boat-like front face.
Development went on from 1936 to 1939 with the first 7 vehicles completed in July 1940 and 14 more by March 1941. In addition to 3 men seated in tandem at the front and crew 20 passengers could take place at the back in the gallery. The vehicle however was certainly a heavy prey on land: Massive, unarmored and ponderous, it was a heavy prey in any combat area. Late prodction vehicles differed by having new suspension springs and four return rollers, with Drive sprocket like the Panzer IV. The early version had leaf springs recalling the Panzer II, and three return rollers. The LWS was propelled at sea by a Maybach HL120 V12 engine petrol with a 11,867 cc (724in3) capacity; rated for a 300 hp (224 kW) output at 3,000 rpm, procuring a Power/weight ratio of 8.8 hp/t. There was an observation sea in a tower behind the crew's compartment, with possibly a ring-mounted MG.34, although no photos shows it. It was surrounded by a wavebreaker kiosk and therefore most probably used for guidance at sea in heavy weather as the lower compartment was probably blinded by spray. The vehicle was unarmed, but those carried by the infantry, which could be deployed on the deck. The central compartment was like a bathtub with the boat hull built around to procure buoyancy, so usuful espace was lost there. Just like a boat, the vehicle could be given naval accessories such as buoys, anchors, rubber dingy, rim padding, and steel cable.
It all boiled down to a demonstrated to General Franz Halder, on 2 August 1940. It was organized by the Reinhardt Trials Staff on the island of Sylt (an island in northern Germany, Nordfriesland, Schleswig-Holstein). The general was impressed by the general concept but critical about the tall silhouette on land. He concluded the overall usefulness was clear and proposed to push forward to the OKW that enough LWSs would be available, basically one for two invasion barges. However it was a difficult vehicle to mass-produce, and by the time Rheinmetall-Borsig had devlivered enough of them, Sealion has been postponed. This protracted development could have led to the cancellation of the Landwasserschlepper, but it nevertheless entered service in 1942 and was deployed both in Russia and North Africa in small numbers. By 1944 a new design was created, called the LWS II. It was based on the Panzer IV chassis, featuring a small raised armored driver's cabin and flat rear deck. The engine was fed in air by four fold-down intakes and expussed combustion gasses through exhaust stacks. It was never authorized as there were more pressing issues, and priority was given to tank hunters by that point. Nevertheless, the Landwasserschlepper stayed operational until the end of the war.

Landwasserschlepper LWS-II

An LWS I in North Africa, 1942
Specs. Landwasserschlepper |
|
| Dimensions : | 8,60 x 3,16 x 3,13 m (28 ft 3 in x 10 ft 4 in x 10 ft 3 in) |
| Total weight, battle ready : | 13 tonnes (17 loaded). |
| Crew : | 2 +20 passengers) |
| Propulsion : | Maybach HL120 V12 petrol, 300 hp +4-cyl boxer 25bhp |
| Speed : | 35 km/h (21 mph) road, 12 km/h (7½ mph) water |
| Range (road) : | 150 km |
| Total production | 100 |
Src and links
https://web.archive.org/web/20111118001215/http://news.webshots.com/album/556523742Ddfftchttp://panzerserra.blogspot.com/2013/03/landwasserschlepper-lws-amphibious.html
Fitzsimons, Bernard, ed. (1978). Illustrated Encyclopedia of 20th Century Weapons and Warfare, Vol. 16.
Hogg, Ian; John Weeks (1980). Illustrated Encyclopedia of Military Vehicles. London
Schenk, Peter (1990). Invasion of England 1940: The Planning of Operation Sealion. Conway Maritime Press Ltd.
Trojca, Waldemar; Markus Jaugitz (2008). LWS: Land-Wasser-Schlepper. Model Hobby.
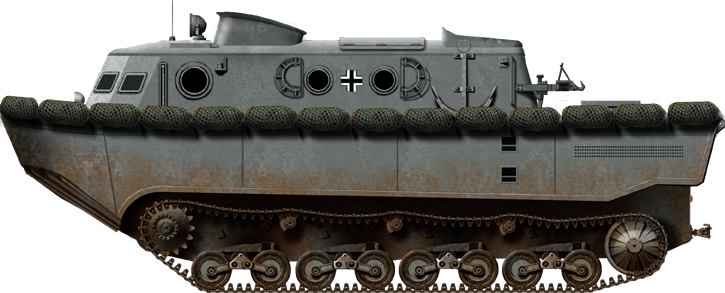
Landwasserschlepper in regular marine grey livery as built.

A camouflaged vehicle used on the baltic coast

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com