GERMAN ARMOUR WW2
Note: This is the old historic archive (2011) Archived articles (and upcoming)
Archived articles (and upcoming)
Aftermath of the Versailles treaty
During WW1, after the initial shock, the Germans paid little attention to the idea of tanks in trench warfare. They mostly relied on special infantry units to perform breakthroughs, like the famous Sturmtruppen. It was thought that tanks were too vulnerable1. However, after the successes of isolated British tanks, which made their way into German lines, they first began to consider an appropriate response, and then a tank of their own. The A7V, a mobile fortress, was their only successful attempt in this direction, and only a handful were produced until the armistice. Several light tanks were also considered, but none reached production in time. In 1919, the drastic Versailles treaty imposed severe limitations on military personal and material, and it also forbade tank construction. Only a handful armored cars were retained for police duties.Later on, in 1933, maneuvers incorporated "dummy tanks", until the industry would be ready to work on the first indigenous model. Many models were developed in Sweden or the Soviet Union, earning some much valued experience. In 1934, the first Panzerkampfwagen I was issued to the Wehrmacht, with the ordnance (Waffenamt) designation Sd.Kfz. 101. Two years later, the German tank force was augmented by the Panzer II and the first Panzer IIIs. There were capable against the armored vehicles of neighboring powers, like Czechoslovakia and Poland, but not against those of France, and even less against the USSR.
Articles
Tanks
Panzer I * Panzer II * Panzer 35(t) * Panzer 38(t) * Panzer III * Panzer IV * Panzer V Panther * Panzer VI Tiger I * Panzer VI Tiger IIJagdpanzers
Panzerjäger I * Marder-I * Marder-II * Marder-III * Jagdpanzer 38 Hetzer * Ferdinand/Elefant * Jagdpanzer * Jagdpanzer-IV * Jagdtiger Tiger Ausf B * Nashorn * Sturer EmilSelf Propelled Artillery
StuG III * StuG IV * Grille * Wespe * StuIG 33B * StuH 42 * Karl-Gerät * Sfkfz-4 Panzerwerfer * Grille * Wespe * Dicker Max * Stpzr-IV Brummbär * Sturm TigerFlakPanzers
FlakPanzer I * Flakpanzer 38(t) * FlakPanzer III * FlakPanzer IV Wirbelwind * Flakpanzer IV Möbelwagen * Flakpanzer IV Ostwind * Flakpanzer IV Kugelblitz * 2 cm Flak 30 auf Sd.Kfz.10 ➹ * Merc. L4500a Flakwagen ➹Armoured Cars
ADGZ * Sd.Kfz-231 6-rad * Sd.Kfz.247 * Sd.Kfz.263 * Sd.Kfz.254 * Leichte Radschlepper laffly W 15T(f) * Bunkerflak * Kfz.13 * Sd.Kfz-233 8-rad * Sd.Kfz.234 Puma * Sd.Kfz.247 * Sd.Kfz.250 * Sd.Kfz.251Misc.
Projects & prototypes * Maus * Landwasserschlepper * Wurfrahmen 40 * BergePanzer III * BergePanzer IV * Bergepanther * BergeTiger * Bergepanzer 38(t) * Bergepanzer T-34 * Landwasserschlepper II * Karl-Gerät * Goliath * Springer * Borgward IV * VK 20 series * VK 4502 (P) * Gep. MTW Kätzchen * Enwicklung seriesGerman Vehicles
VW Kübelwagen * VW Schwimmwagen * Kettenkrad SdKfz.2 * SdKfz.3 Maultier * SdKfz.6 * SdKfz.6/2 FLAK 37 * SdKfz.6/3 * Sd.Kfz.7/1 FV38 * Sd.Kfz. 7/2 FLAK 36 * Feuerleitpanzer auf Zugkraftwagen 8t * Sd.Kfz.9/1 ARV * 8.8 cm Flak 18 auf SdKfz.8 * Sd.Kfz.10 gepanzert * 8.8 cm Flak 18 auf SdKfz.9 * Sd.Kfz.10 gepanzert * SdKfz.10 * SZwgn-12 DB10 Gpz * Somua MCG (S307(f) * Somua MCL (S303(f) * Unic TU1 U305(f) * Schwere Geländegängiger Lastkraftwagen 4.5t Mercedes-Benz L4500A als FlakwagenPanzer development (1936-45)
Tanks available prior to the Campaign of France (1940)
The Panzer I and II were considered transitional models, designed for training and to prepare the industry for future, more advanced, vehicles. Despite this, they were forced into combat, mostly as scout vehicles. The Panzer II remained in service for quite a long time. But the real game changer was the Panzer III. After a long elaboration, both technical and theoretical, this first true German medium tank entered mass production quite late, with the Ausf. E/F versions in 1939. Until the Ausf. L upgrade, all mounted the same 37 mm (1.46 in) main gun, completely inefficient against the well armored medium tanks of the Allies, and the armor was quite weak. But these drawback were compensated by many other qualities, including reliability, speed, a radio and a three-man turret.The Panzer III, after armor and gun upgrades, formed the bulk of the Wehrmacht, until late 1942. By then, another model became available in great numbers, the Panzer IV. Conceived by Guderian and developed in 1936 as a support medium tank (Begleitwagen), it was available in limited quantities during the battle of France, but formed a large part of the Wehrmacht in the summer of 1941, during Operation Barbarossa. It borrowed many components from the Panzer III, but mounted a 75 mm (2.95 in) howitzer intended to deal against fortified positions. In this Wehrmacht duo, the Panzer III was intended to deal with other tanks, while the Panzer IV provided infantry support. But as the limitations of the former became evident, the latter was quickly upgraded with long-barrel, high velocity AT guns. This model became the mainstay of the German armor until 1945.
Operation Barbarossa: The Eastern Front (1941-42)
When German officers received alarming reports of Soviet "invincible tanks", investigation followed on some captured KV-1s and T-34s. For the first time, an unpleasant feeling of inferiority spread through the Wehrmacht, especially after the merciless winter of December 1941-February 1942. Under the insistence of Hitler and Eastern Front generals, two new design were quickly put on the drawing board. The Panzer V, also called the Panther, and the Tiger, or Panzer VI were meant as an answer to the shortcomings of their predecessors. Both were equipped with excellent guns. The Tiger's KwK 36 was an adapted anti-aircraft gun, with ultra-high velocity, excellent range and new specially crafted armor-piercing and hollow-charge shells, notably the costly tungsten rounds. Both tanks first appeared after a year and a half development, and they were ready in time for the battle of Kursk, in July 1943. They gave cold sweats to the Russian tank crews, as well as the Allies later, in Italy and France.New generation: Panther and Tiger (1943)
Both the Tiger and the Panther were, on paper, some of the best designs in the world when they came into service. However, both of them suffered from serious teething problems due to them being rushed into production and to the front lines. The Panther became the second most produced German tank of the war, but neither of these vehicles was produced to the numbers reached by the Allied tanks. While this is generally attributed to a German "quality is better than quantity" thinking, it was actually due to a long list of factors, ranging from demographics, war bombing, the way the German industry was set up and German military thinking.Costs speak for themselves. While a Panther was only a little more costly than a Panzer III (117,000 RM vs 91,000 RM) the Tiger was twice as costly (250,000-300,000 RM). The very early series, still incorporating uniquely designed parts and accumulated development costs, were probably up to eight times more costly than the average StuG. But, with parts commonality and simplification, new modular production methods, and a huge, expendable forced labor force (from concentration camps), a significant numbers of each model was built until the end of the war. If the Panther was the most cost-effective German AFV, and perhaps the most effective tank of WW2, the Tiger made such an impression, that it quickly shaped its own legend, besides any propaganda effort. For its time, it was a hardened steel mobile bunker, equipped with one of the most awe-inspiring guns of the war, the German anti-aircraft 88 mm (3.46 in). The before feared T-34 and many Allied tanks, including the M4 Sherman, were now easy targets from up to three miles away. With limited availability, this machine was only given to young, highly motivated crews.
The Tiger had serious tendencies to breakdown, was slow and had a limited range due to very high consumption figures. The complicated drivetrain was difficult to repair, as were the tracks. Moreso, Tigers disabled and abandoned were often lost for good, as towing was difficult. However, the large tracks were an advantage on soft grounds (snow and mud), lowering ground pressure. In fact both tanks incorporated a great deal of wartime learnt improvements.
Turretless Panzers: A misjudged success story
Both the Panzer III and IV were quite expensive, and new mass-producible, cheaper variants for infantry support and tank-hunting were sought. The most expensive part of these models, the turret, was replaced by a new, lowered hull, in the StuG III and IV, and their tank-hunter equivalents. Ultimately, with versions equipped with the 75 mm (2.95 in) short-barrel howitzer or AT guns like the Pak 40, the StuGs formed a growing part of the AFV production by 1943, and were the unsung metal heroes, the jacks-of-all-trade of the Wehrmacht. More robust, more difficult to hit, easier to repair, they added their numerical advantage, with no sacrifice to quality. The average cost of the StuG III was 80,000 RM, compared to 95,000 for a regular Panzer III. With 9400 StuG IIIs, 1200 StuH IIIs and 1100 StuG IVs, more were built than any other German tank or SPG of the war. Some StuGs were used extensively as tank-hunters, and proved more lethal even than the Tiger, with some 20,000 kills credited to these small hunters. They simply used shorter range and ambush tactics, enabled by their lower silhouette, easy to camouflage.Panzerjägers: Hunting spirit
As soon as the fall of Poland, German planners thought of converting existing platform in order to mount heavier ordnance than the regular 37 mm (1.46 in) PaK 36, especially to deal with the well protected French and British tanks during the upcoming campaigns. At this point, they looked upon the excellent Czech AT 47 mm gun (1.85 in), already available in quantity, and mounted it on the Panzer I chassis. Soon after, the elderly Panzer II chassis was chosen to carry the 7.5 cm (2.95 in) PaK, as the Marder II as did some captured French models (Marder I). The Czech 38(t) provided two other variants, Marder III and the famous Jagdpanzer 38(t) (ubiquitously and incorrectly known as the Hetzer). The Panzer IV chassis allowed the construction of a low-profile turretless vehicle using the StuG recipe, armed with with a long barrel high velocity PaK 39, the Jagdpanzer IV. Attempts to use the deadly 88 mm (3.46 in) gave birth to several other variants.The Nashorn (also called Hornisse), was an adaptation of the Panzer IV chassis with said gun. The later stages of the war gave birth to more advanced vehicles, like the Jagdpanther, Elefant, and Jagdtiger. The latter, only produced in small numbers, was equipped with the most awesome piece of anti-tank artillery ever carried during the war, a 128 mm (5 in) gun. The tank itself, weighing nearly 72 tons, had a high consumption, suffered a lot of breakdowns, and was tactically difficult to move, as it was forbidden from crossing many bridges.
Later Panzers and the defensive war (1944-45)
Numbers alone were not enough during WWII. In face of odds rarely encountered by an army, of ten to one numerical inferiority on almost every front in 1944-45, the Germans slowly gave way until the end, while exacting heavy tolls on the Allies. But the ultimate defeat was quickened thanks to a near total air superiority and new Allied tank-hunters. The British 6-pdr gun proved lethal against the Axis war machines, and was subsequently employed by many US and British tank destroyers. The Soviets were able to field many SU-85s and SU-100s in 1943, also equipped with an adapted, former AA gun. The next generation tanks, the T-34/85, IS-1 and IS-2, also came en masse in 1944. Thus, some some real killing power was added to the numerical advantage on Soviet side.Despite the lack of resources required to produce even the Tigers, Hitler insisted for more gargantuan models. As soon as 1943, a replacement for the Panzer VI was designed. An even more impressive heavy tank, the Tiger II or KönigsTiger. This nearly 70 tons monster incorporated some features from the Panther and an even more powerful and lethal gun. As the engines were still not up to the task, mobility was, once again, an issue. Plus, these new tanks were even more costly, and the Allied bombardment campaign began to take its toll. As the future in the east looked bleaker, Hitler and his generals looked west. The plan was simple and daring. All available Panzer VIs, one of Hitler's cherished "Wunderwaffe", were supposed to be gathered in a single Panzer division, the spearhead of a new unstoppable force. The objective was to pierce the weakest point of the US sector defensive line, in the Ardennes, in Belgium, and once again achieve the 1940 masterstroke, a rush to the sea, ultimately cutting off the supplies of the Allied forces. The ultimate goal was, in Hitler's mind, to negotiate, in favorable terms, a separate peace with the western powers, and to concentrate all efforts on the Eastern front.
Last projects
The Panzer VII was named the "Löwe", a 76-90 ton heavy tank, of which none were built. The project was cancelled. Another Hitler "Wunderwaffe" was a super-heavy tank named at first "Mammuth", but then, by derision, "Maus". Weighing close to 200 tons, powered by a gargantuan diesel and sporting a monstrous 128 mm (5 in) gun, this was the ultimate Wagnerian war machine. However, with long-lasting trials, relatively weak performance, and many problems to cope with, like huge consumption, slow speed, weak maneuvering capabilities and ultra-high cost, the entire project was cancelled in 1944. Other even more impressive giants never hopped of the drawing board, like the P1000 "Ratte", also known as the "Landkreuzer". This gigantic "land cruiser" was, on paper, propelled by two U-Boat diesel engines, and armed with a naval battleship turret, firing two 280 mm (11 in) guns, with a 128 mm turret and quite an impressive array of AA artillery. It was a late rebirth of the very early tank concepts of tanks, inspired by H.G. Wells' novel.Another project was the E 100, supposedly a lighter and faster version of the "Maus", but, weighin 140 tons, it was still unrealistic in 1944. A single prototype was captured by the British before reaching completion. But the all-category champion was the P-1500 "Monster", a 1500 ton gun carriage fielding no less than the Schwerer Gustav, able to fire a 800 mm (31.5 in) shell at 39 km. A big waste of resources was used to forge the superhuman, oversized tracks (more or less similar to those used later by NASA Saturn V pod carrier), which were all that remained of it.
Featured AT guns
From 1933 to 1945, the Wehrmacht took delivery to tens of thousands of antitank guns, from the puny standard 37 mm to the legendary 8.8 cm Pak 43 extrapolated from the AA gun.
PAK-36: 12,000 were built of this light standard infantry AT gun which was the ordnance main issue. Infamously called "door-knocker device" in the 1940 campaign because of its poor perforlances against heavily-armored allied tanks, it was sufficient against lighter armoured vehicle and stayed into service to the last day of the war, recycled to fire shaped-charges like the Stielgränat 41.
The wartime German arsenal comprised in all 15 models registered, like the unusual 2.8 cm sPzB 41, the very common 7.5 cm Pak 40, or the fearful 8.8 cm Pak 43.

-2.8 cm sPzB 41: Basically a super-high velocity tapering barrel gun of "real" 20mm caliber. Despite this small caliber, it could launch a projectile 4,500 feet per second (1,400 m/s) at 500m, capable of piercing 52 to 69 mm of hardened steel inclined at 70° at 100m. About 2,797 were built by Mauser. It was a development of the experimental Gerlich's coned-bore barrel 7 mm anti-tank rifle.
-4.2 cm Pak 41: Basically an airborne version of the regular Pak 36, but using the same squeeze bore principle as described above for a real final caliber of 28 mm. Only 313 were delivered. They could defeat 87 mm of straight armour at 500m.
-4.7 cm Pak 38(t): Captured Czech AT gun, which famously equipped the Panzerjäger I during the French campaign and catpured R35 tanks. Also called 4,7cm KPÚV vz. 38 originally production resumed in 1940 by Skoda Works, and its 775 m/s (2,542 ft/s) muzzle velocity gave the ability to defeat 60 mm of hardened steel (2.4 in) @ 1,200 metres (1,300 yd).
-4.7 cm Pak 181(f): Captured french AT gun originally called 47 mm APX anti-tank gun which also equipped the Char B1 and S35. It had a 855 m/s (2,805 ft/s) muzzle velocity.
-7.5 cm Panzerabwehrkanone 97/38: Captured French AT gun (the venerable 1898 "soixante-quinze") was declined as an AT gun with pneumatic tires and tailored shield. Originally 4500 Canon de 75 Mle 1897/33s were in service in WW2 in France alone, and it was also the main dual-purpose gun of the Polish Army. The Germans have these modified by a new muzzle brake and mounted on a 5 cm Pak 38 carriage, then sent to the Eastern front. But they lacked modern AP shells and had a low muzzle velocity. The unmodified ones were named in German service 7.5 cm Pak 97/38(f).
-5 cm Pak 38: Early standard German AT gun (9500+) produced by Rheinmetall until 1945. Best results obtained with Panzergranate 40 APCR shots with a hard tungsten core. Muzzle velocity 550-1,130 m/s (1,804-3,707 ft/s), 3000 yards range.
-7.5 cm Pak 40: German standard WW2 AT Gun, more than 20,000 built until 1945. Effective at 1,800 metres (5,906 ft) in direct fire, with the APCR round muzzle velocity was 933 m/s, it could penetrate 154 mm of straight hardened steel at 500m. Rounds in use were the PzGr. 39, PzGr. 40 and PzGr. 38 HL/B (HE shell). Was used also by Finland and Hungary.
-7.5 cm Pak 41: Krupp Semi-experimental (150 built until 1943) and using the Gerlich principle: Real diameter was 55mm. With the AP round muzzle velocity was 1,230 m/s (4,035 ft/s), and it was effective at 2200 yards. It could penetrate 172 mm @30° at 500m.
-7.5 cm Pak 42: Also used on the Panther (Kwk 42). Can use the Panzergranate 39/42 (Pzgr. 39/42), Panzergranate 40 (Hk) (Pzgr. 40/42) and Sprenggranate 42 (Sprgr. 42) (HE). Best performances with the Pzgr. 40/42 (APCR) reaching 1,130 m/s (3,700 ft/s), penetrating 234 at 500m. Production unknown.
-7.62 cm Pak 36(r): Captured Soviet gun, about 560 converted. These 76-mm divisional guns model 1936 (F-22) were originally designed as field gun but with AT capabilities in mind. Best performances were obtained with the German-built 7.62 cm Pzgr.40, which can penetrate 158mm of 60° hardened steel at 500m and more.
-8 cm PAW 600: Semi-experimental high-low pressure gun firing hollow charges, developed by Rheinmetall. 260 Built 1943-44. Could fire at 520 m/s (1,706 ft/s) and 700m effective range and armor penetration was 140mm of vertical armor with a common shaped-charge 8 cm W Gr Patr H1 4462.

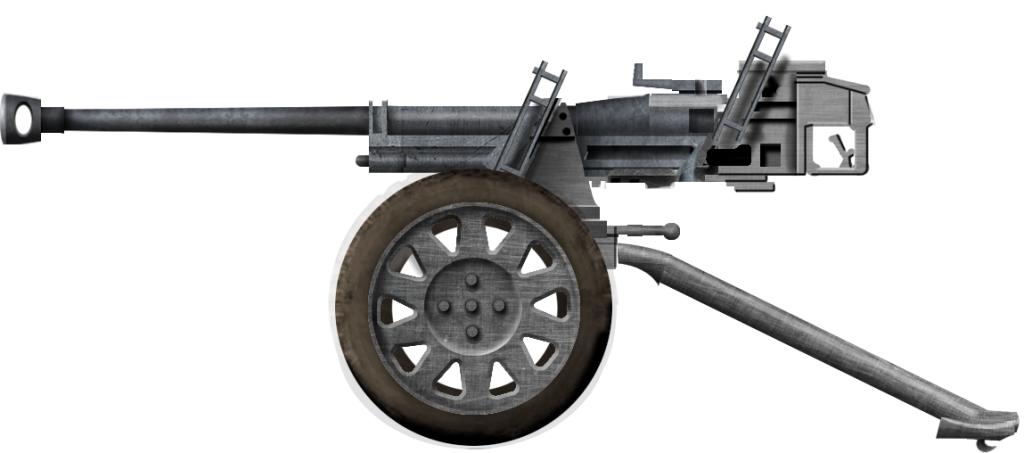
-8.8 cm Pak 43:
AT adaptation by Krupp and Rheintemall of the legendary anti-aircraft 88mm gun. Produced to about 2,100 until 1945. Use a tailored carriage of the cruciform quad mount. Effective at 2000m and more in almost flat trajecories it could fire indirectly at 15,000m. Could fire the versatile Pzgr. 39/43 APCBC-HE (can penetrate 185 mm at 500m) or the Pzgr. 40/43 APCR (penetration 217mm at 500m, up to 153 mm at 2000m with almost 50% first hit capability.
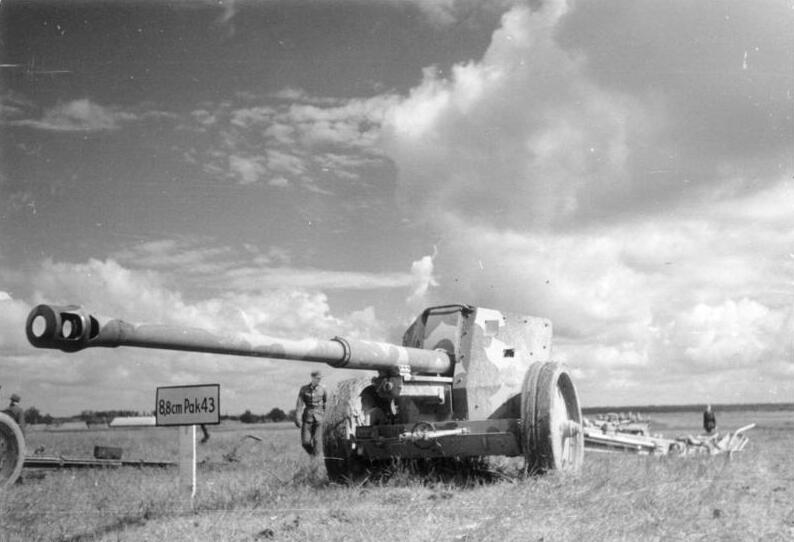 -12.8 cm Pak 44: Most massive AT gun in use by the Werhmacht, produced by Krupp to just 51 unit until 1945. Variation of the type used on the Jagdtiger. Can fire about the same ammunitions and figures similar to the 8.8 cm Pak 43 but long range results were better. It was capable to penetrate 230 millimetres (9.1 in) 30° at 1000 m. Used a quad (two axles), two-legged mount.
-Recoiless guns: 7.5 cm LG 40, 10.5 cm LG 40 and 10.5 cm LG 42. The latter had a muzzle velocity of 195 m/s (640 ft/s) or 335 m/s (1,099 ft/s) depending on the projectiles. These were light, portable guns for airborne units, best used against infantry as penetration power was rather poor.
-FLAK guns used in casual AT role: 2 cm Flak 30/38/Flakvierling 2 cm Gebirgsflak 38 3.7 cm Flak 18/36/37/43 5 cm Flak 41 8.8 cm Flak
18/36/37/41 10.5 cm FlaK 38 12.8 cm FlaK 40. The 88 was famously deployed in France by Rommel to stop the rampaging British Mathilda at Amiens and in several other occasions in North Africa and the Eastern Front.
-12.8 cm Pak 44: Most massive AT gun in use by the Werhmacht, produced by Krupp to just 51 unit until 1945. Variation of the type used on the Jagdtiger. Can fire about the same ammunitions and figures similar to the 8.8 cm Pak 43 but long range results were better. It was capable to penetrate 230 millimetres (9.1 in) 30° at 1000 m. Used a quad (two axles), two-legged mount.
-Recoiless guns: 7.5 cm LG 40, 10.5 cm LG 40 and 10.5 cm LG 42. The latter had a muzzle velocity of 195 m/s (640 ft/s) or 335 m/s (1,099 ft/s) depending on the projectiles. These were light, portable guns for airborne units, best used against infantry as penetration power was rather poor.
-FLAK guns used in casual AT role: 2 cm Flak 30/38/Flakvierling 2 cm Gebirgsflak 38 3.7 cm Flak 18/36/37/43 5 cm Flak 41 8.8 cm Flak
18/36/37/41 10.5 cm FlaK 38 12.8 cm FlaK 40. The 88 was famously deployed in France by Rommel to stop the rampaging British Mathilda at Amiens and in several other occasions in North Africa and the Eastern Front.Tank guns in use were the 2 cm KwK 30 (like on the panzer II), Czech 3,7cm ÚV vz. 38 (used on the Panzer 38(t), 5 cm KwK 38 5 cm, KwK 39 7.5 cm, KwK 37 7.5 cm, KwK 40 7.5 cm, KwK 42 8.8 cm and KwK 36 8.8 cm KwK 43 used from the Panzer III to the Panzer VII Königstiger.
Light tanks
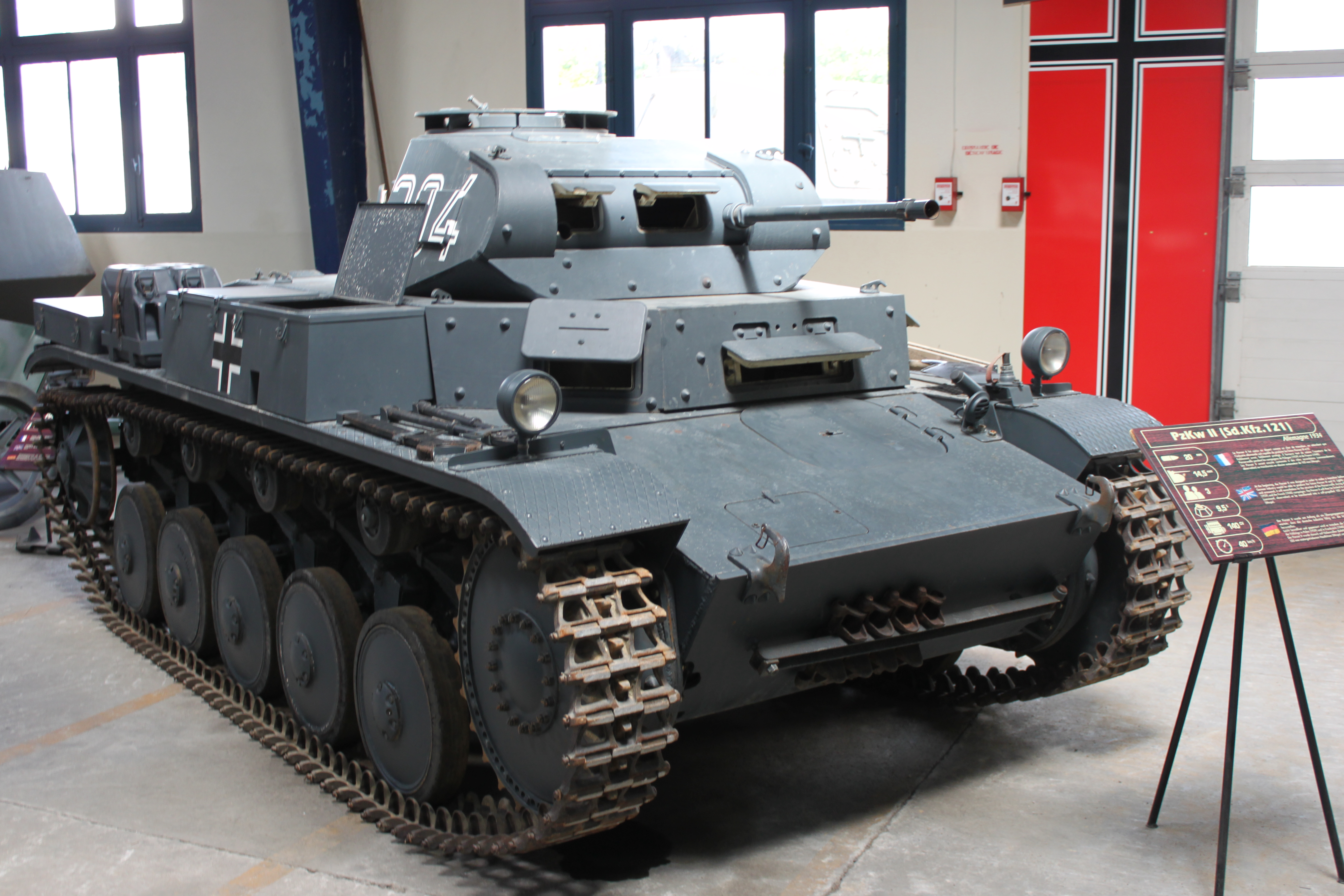

The Panzer II was a provisional, stopgap model, which was mostly used as a scout tank during the war. Late models, like the "Luchs" (Ausf. L), shared nothing but the name with the previous versions.
- Panzer I (1934)
1493 built. Two MG 34 machine-guns. The main variants were the Ausf. A and B, and the wartime variants C and F were built in limited numbers. Four variants emerged, a command tank, a SPH (sIG 33 Bison), an AA tank (FlakPanzer I) and a tank-hunter (Panzerjäger I).- Panzer II (1935)
1856 built. One 20 mm (0.79 in) autocannon, one MG 34. It consisted of a preseries, the Ausf. A/B/C main variants, while the wartime variants F and L (Luchs) were built in small numbers. The J was heavily armored. Many derivatives emerged, including a tank-hunter (Marder II), a gun motor carriage (Wespe), a howitzer heavy motor carriage (sIG-33 Bison) and a flame-thrower version (Flamingo).Medium tanks
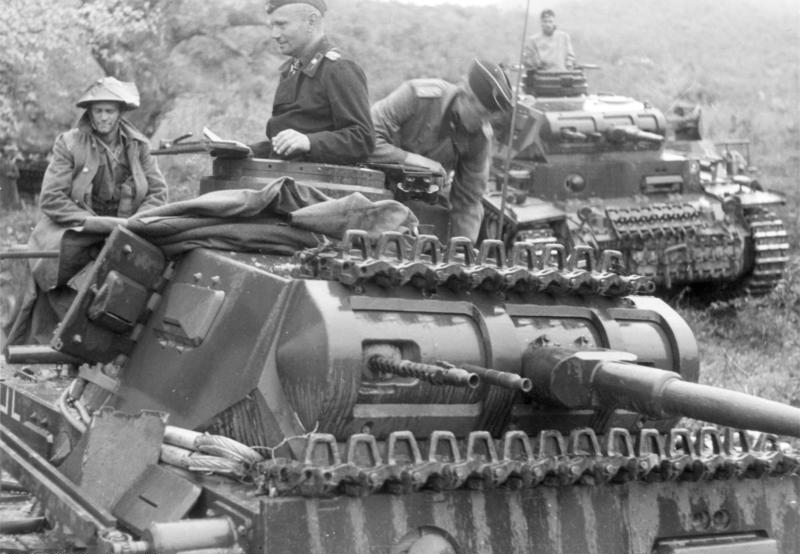 The Panzer III was, until 1942, the mainstay of the German armor. However, because it was unable to house bigger, longer barrel guns, it was replaced by the Panzer IV as the German main battle tank. Production of models based on its chassis flourished, notably with the StuGs series. In this photo, New Zealand prisoners pass near a Panzer III command version of the 2.Pz.Div. in Greece, near Pandelejmon, April, 16, 1941.
The Panzer III was, until 1942, the mainstay of the German armor. However, because it was unable to house bigger, longer barrel guns, it was replaced by the Panzer IV as the German main battle tank. Production of models based on its chassis flourished, notably with the StuGs series. In this photo, New Zealand prisoners pass near a Panzer III command version of the 2.Pz.Div. in Greece, near Pandelejmon, April, 16, 1941.
- Panzer III (1936)
5774 built, One 37 mm (1.46 in), 50 mm (1.97 in) or 75 mm (2.95 in) gun and three MG 34s. Ausf A to N variants, plus command tanks, special versions and derivatives (StuG III, tank hunters and howitzer motor carriages).- Panzer IV (1936)
8800 built, One 75 mm (2.95 in) short barrel howitzer or long-barrel gun, and two MG 34s. Ausf A to J variants, plus Brummbär (Sturmpanzer) heavy gun carriage, JagdPanzer IV tank-hunter, StuG IV and Wirbelwind AA version.- Panzer V Panther (1942)
6000+ built, One 75 mm (2.95 in) KwK 42 L/70 gun, two MG-34s. Ausf. D, A and G variants. Tank hunter derivative (Jagdpanther).Heavy tanks
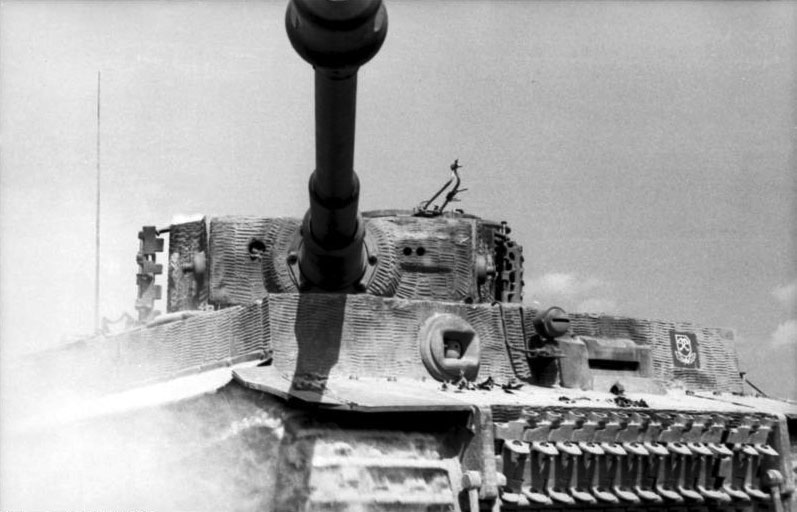 A Panzer VI Tiger of the 101st Abteilung in Northern France, late 1944. The Tiger was probably the most feared machine in the German arsenal. Its armor ranged from 100 to 120 mm (3.93-4.72 in) and the velocity and range of the 88 mm (3.46 in) gun gave its crew immense confidence in combat. Allied tanks were seen as sitting ducks. Some of its commanders became aces, like the famous Michael Wittman.
A Panzer VI Tiger of the 101st Abteilung in Northern France, late 1944. The Tiger was probably the most feared machine in the German arsenal. Its armor ranged from 100 to 120 mm (3.93-4.72 in) and the velocity and range of the 88 mm (3.46 in) gun gave its crew immense confidence in combat. Allied tanks were seen as sitting ducks. Some of its commanders became aces, like the famous Michael Wittman.
- Panzer VI Tiger (1942)
1347 built, One 88 mm (3.46 in) KwK 36, two MG 42s. Ausf H and E variants.- Panzer VI Ausf. B Königstiger (1943)
492 built, One 88 mm (3.46 in) gun, two MG 42s. Jagdtiger tank-hunter derivative. Durchsbruchswagen II or Prototype DW 2, as delivered with the Krupp Turm (1940).
Durchsbruchswagen II or Prototype DW 2, as delivered with the Krupp Turm (1940).
 Prototype VK 36.01 chassis, Kummersdorf testing ground, fall 1941.
Prototype VK 36.01 chassis, Kummersdorf testing ground, fall 1941.
 Prototype VK 45.01 (1942), Porsche Tiger prototype.
Prototype VK 45.01 (1942), Porsche Tiger prototype.
 The only Porsche Tiger in active service with Abt.653, Ukraine, June 1944.
The only Porsche Tiger in active service with Abt.653, Ukraine, June 1944.
Super heavy tanks
- Panzer VIII Maus (1944)
2 built (prototypes) One 128 mm (5.03 in) and one 75 mm (2.95 in) gun. Cancelled.- P.1000 Ratte (1942)
Project of a "landkreuzer" of 1000 tons, cancelled.Tank destroyers (Panzerjäger)
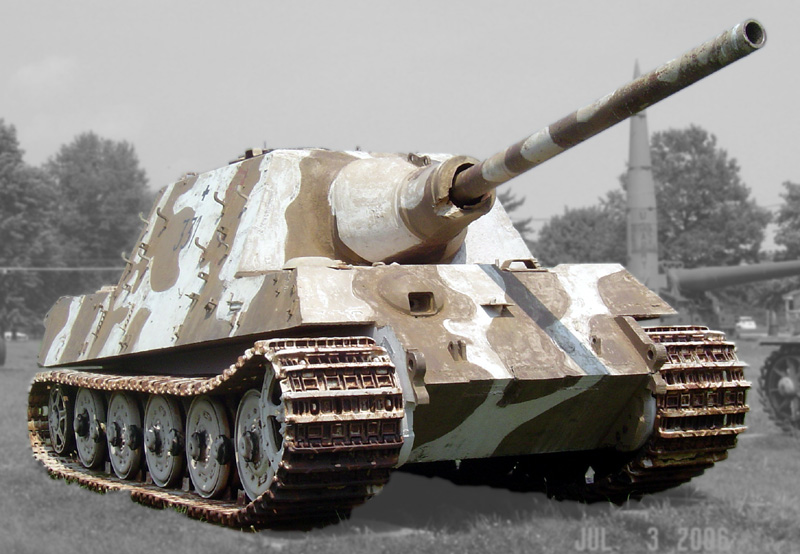

The awesome Jagdtiger. Only a handful of these beasts were ever produced, and their weight made them near-impractical. Engine limitations led to a lot of breakdowns. But when in place, their protection, firepower and range were unrivaled until the end of the war - Credits: Wikipedia.
- Panzejäger I (1940)
202 built, based on Panzer I wit one 47 mm (1.85 in) gun.- Marder I (1942)
170 built, based on a Lorraine 37L, Hotchkiss H39 or FCM 36 chassis. One 75 mm (2.95 in) gun.- Sd.Kfz. 132 Marder II (1942-43)
201 built or converted, based on the Panzer II Ausf. D/E 76.2 mm (3 in) PaK 36(r) gun.- Sd.Kfz. 131 Marder II (1943-45)
651 built or converted, based on the Panzer II Ausf. A/B/C and F. One 75 mm (2.95 in) PaK 40 gun.- Marder III (1942-43)
363 built, based on the Czech 38(t)chassis. One 75 mm (2.95 in) PaK 40 gun.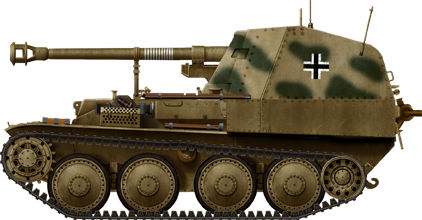 One of the three variants of the Marder III, based on the excellent Panzer 38(t) chassis manufactured by BMM (Skoda). The Ausf.M was built on one of the later chassis, sharing the front engine configuration with the Grille Ausf.M. Like the other Marder IIIs, it was armed by the standard 7,5 cm Pak 40, and not with the Russian Soviet 76.2 mm field gun of the first Marders. This gun was found able to penetrate the armor of the T-34 and KV-1 at that time. The gun was mounted in a rear casemate, with its own shield for added protection. It was emerging from a large opening in the frontal armor for better traverse. It also had a lower profile, and was also the most largely produced, with 942 vehicles from May 1943 to May 1944.
One of the three variants of the Marder III, based on the excellent Panzer 38(t) chassis manufactured by BMM (Skoda). The Ausf.M was built on one of the later chassis, sharing the front engine configuration with the Grille Ausf.M. Like the other Marder IIIs, it was armed by the standard 7,5 cm Pak 40, and not with the Russian Soviet 76.2 mm field gun of the first Marders. This gun was found able to penetrate the armor of the T-34 and KV-1 at that time. The gun was mounted in a rear casemate, with its own shield for added protection. It was emerging from a large opening in the frontal armor for better traverse. It also had a lower profile, and was also the most largely produced, with 942 vehicles from May 1943 to May 1944.
- Sturmgeschütz IV (1942-44)
1139 built, based on the Panzer IV chassis. One 75 mm (2.95 in) PaK 40 gun.- Jagdpanzer IV (1943-45)
2000 built, based on the Panzer IV chassis. One 75 mm (2.95 in) PaK 42 gun.- Jagdpanzer 38(t) (1944-45)
2827 built, based on the Czech 38(t) chassis. One 75 mm (2.95 in) gun.- Nashorn (1943-44)
473 built, based on Panzer III/IV chassis. One 88 mm (3.46 in) gun.- Elefant (1943)
91 built, based on the rejected Porsche Tiger chassis. One 88 mm (3.46 in) gun.- Jagdpanther (1944-45)
415 built, based on the Panzer V Panther chassis. One 88 mm (3.46 in) gun.- Jagdtiger (1944-45)
88 built, based on the Panzer VI KönigsTiger chassis. One 128 mm (5 in) gun.- Sturer Emil (1942-43)
2 built, based on a Henschel chassis with a 128 mm (5 in) gun.Gun motor carriages
- sIG-33 Bison (1940)
38 built, based on Panzer I. One 155 mm (6.1 in) howitzer.- 15 cm sIG 33 auf Fahrgestell Panzerkampfwagen II (Sf) (1941)
Also incorectly known as the Sturmpanzer II or Bison II. 12 built, based on the Panzer II.-Sd.Kfz.124 Wespe (1941-42)
682 built, based on the Panzer II. One sIG 33 155 mm (6.1 in) howitzer.- StuIG 33B (1941)
24 built (Sturm-Infanteriegeschütz 33B), based on the Panzer III. One 155 mm (6.1 in) howitzer.- StuG III (1942-45)
9408 built, based on the Panzer III, with a 75 mm (2.95 in) gun.- StuH 42 (1942-44)
1211 built (Sturmhaubitze 42) , based on the Panzer III, with a 105 mm (4.13 in) howitzer.- Sturmpanzer IV Brummbär (1944-45)
306 built, based on the Panzer IV, with a 150 mm (5.9 in) StuH 43 howitzer.- Sturmtiger (1943-44)
19 built (Sturmmörserwagen 606/4 mit 38 cm RW 61), based on the Tiger, with a 380 mm (15 in) rocket launcher.Karl mortar (1940-42)
7 built. The epitome of the self-propelled gun during the war, only seven units of this gargantuan self-propelled siege mortar were built between 1940 and 1942, but its development goes back to 1937. Originally, Rheinmetall proposed a super-heavy howitzer to attack the Maginot Line. It was decided to make it self-propelled in January 1937, using very long, large tracks and a Daimler-Benz MB 503A gasoline or Daimler-Benz MB 507C diesel engine, which supplied between 4 and 4.8 hp/ton depending on the model. All seven were almost tailor-made and weighed around 120-125 tons, armed with a 600 mm (24 in) howitzer. Each shell weighted almost a ton and was given a 500 kg warhead. Mobility was limited, and it relied on a trailer and crane for ammo. It could also be disassembled and loaded on a special train for long distance transport.- P1500 Monster (1944)
Paper project only, a self-propelled gun intended to carry the huge 800 mm (31.5 in) "Dora".Armored scouts & transports
- Kübelwagen (1940-45)
50,435 built. Famous VW off-road car.- Schwimmwagen (1942-44)
20,000 built. Derivative VW amphibious car.- Sd.Kfz. 221-223 series (1935-44)
3,340 built. Leichter Panzerspähwagen (4 wheels).- Sd.Kfz. 231 6-rad series (1934-40)
200 built. Schwerer Panzerspähwagen (Heavy armored scout - 6 wheels).- Sd.Kfz. 231 8-rad series (1936-44)
1200 built. Schwerer Panzerspähwagen (Heavy armored scout - 8 wheels).- Sd.Kfz. 247 Panzerbefehlswagen (1937-45)
68 built. 4/6 wheeled armored command car.- Sd.Kfz. 250 (1941-45)
13,000 built. Armored half-tracks.- Sd.Kfz. 251 Hanomag (1942-45)
15,252 built. Main German APC of the war.- Sd.Kfz. 254 (1938-40)
140 built. Armored wheel/track hybrid artillery observation vehicle.
SdKfz 254 in Poland, September 1939

SdKfz 254 in North Africa, 1941
Anti-Aircraft vehicles
-FlakPanzer I (1941)
25 built. This rare conversion appeared in 1941, after it became apparent that towed Flak guns were unable to protect moving Panzer columns. This was a conversion of the obsolete Panzer I Ausf B chassis with a 2 cm FlaK 38 L/112.5. 25 were converted by Stowever and used by the 614th Motorized Flak Battalion in Romania.-Flakpanzer 38(t) Gepard (1943)
141 built. This derivative of the prolific Czech Panzer 38(T) was armed with a 20 mm (0.79 in) Flak 38. The Waffenamt designation was Flakpanzer 38(t) auf Selbstfahrlafette 38(t) Ausf.M (SdKfz 140), or Flakpanzer 38(t) Gepard. Given organically, after early 1944, to the AA platoons of each Panzerbatallion.-Möbelwagen (1944)
250 built by Deutsche Eisenwerke until 1945. Based on the Panzer IV (Flakpanzer IV), armed with a 3.7 cm FlaK 43 L/89 in an open platform.-Wirbelwind (1944)
87 to 105 built by Ostbau Werke in Silesia (diverging sources). Quad 20 mm Flakvierling 38 in an open turret based on the Panzer IV chassis.-Ostwind (1944)
43-44 built. Similar model by the same manufacturer, but armed with a single 3.7 cm FlaK 43 L/89.-Kugelblitz (1945)
2-6 built The Flakpanzer IV Kugelblitz was armed with a fully enclosed turret with Zwillingsflak 30mm MK 103 twin anti-aircraft guns. Only a handful were built at the end of the war.Links
Achtung PanzerPanzerpunkt
 Germans Tanks of ww2
Germans Tanks of ww2

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com
