Another upgrade to the BA series
Following the success of the BA-10, the Soviets decided to upgrade the vehicle further. They were going to use a ZiS-5 army truck, which was better suited to rougher terrain than the GAZ-AAA as used on the BA-10. When the final prototype of the BA-11 was developed and tested, small numbers were produced as a pre-series, just before mass production was due to start. As a result of the outbreak of the war, the few produced were to be the only ones ever built, and even despite various upgrades being designed, the BA-11 project was cancelled.Design Process
In the 1930s, Soviet automobile engineers began experimenting with the ZiS-5 truck. One of these experiments meant that the vehicle was shortened, and it was given an improved engine, lower frame, and additional set of rear wheels. Due to this successful experiment, in the winter of 1938, engineers were given the go-ahead to create an armored car based on a very similar chassis, and this process started in the first few days of 1939. At the Izhora Factory, under the direction of N. Baranov, a very sophisticated prototype was produced on the basis of a ZiS-6 truck (petrol engine). It was sent for factory trials shortly after. It was intended to test it in the Winter War along with other prototype vehicles, such as the KV-1, SMK, and T-46. However, the war ended before the BA-11 prototype could be sent out.
A BA-11 being tested at NIIBT testing grounds, 1940. Notice the different shaped engine hatch at the front.
The BA-11D
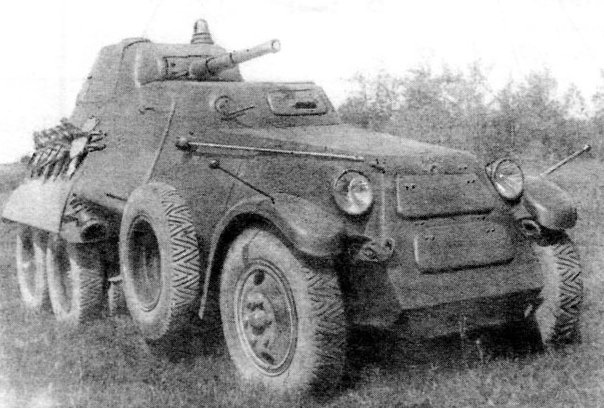

A BA-11D.
After some testing of the vehicle near Moscow, a new prototype was made, reportedly based on the ZiS-34 (a 6x4 version of the ZiS-6 designed in 1940), known as the BA-11D. 16 production model vehicles were produced. There was an intention to mass-produce the vehicle, but the Izhora Factory was cut off from almost all supplies during the Siege of Leningrad, and there was no feasible way for the project to continue with such limited resources.
The BA-11D had armor that was sloped to a greater degree than the BA-10, and the armor was thicker, in order to give better protection, such as the engine compartment hatches being changed. It featured the same 45 mm (1.77 in) gun, but had its ammo capacity increased to 144 rounds. It also featured the same DT machine guns with 3057 rounds each. It was also given bulletproof tires as a minor upgrade. There were some attempts in early 1940 to mount new diesel engines to the BA-11D, but none of these proved successful, and actually made the vehicle slower. Some other chassis were tried out, such as a 6x6 ZiS-36 in autumn 1940, but the outbreak of the war put a stop to this.
The BA-11 in action
The BA-11Ds that were produced were used in the defense of Leningrad. Due to its better armor, similar firepower and substantially better mobility, it was arguably better than the early T-26 models that were in service near Leningrad, and they tended to fare better in combat. On road, the BA-11D achieved double the speed of the T-26. The BA-11D tended to engage enemy armored cars, and gun emplacements. It was actually more fiercely armed than enemy heavy armored cars, but the chassis and engine were simply not good enough to provide the required speed and mobility for the demands of the war, even despite good performance relative to other heavy armored cars.
BA-11D specification |
|
| Dimensions (L-w-h) | 5.3 x 2.5 x 2.4 m (17.4x8.2x7.9 ft) |
| Total weight, battle ready | ~ 8.13–8.65 tonnes |
| Crew | 4 |
| Propulsion | ZiS-16, 93 hp |
| Speed (road) | 64 km/h (40 mph) |
| Range | ~316 km (196 miles) |
| Armament | 45 mm (1.77 in) 20K 2 x 7.62 mm (0.3 in) DT |
| Armor | ~10-13 mm (0.39-0.51 in) Roof - 8 mm (0.31 in) Underneath - 4 mm (0.16 in) |
| Total production | ~18 |

BA-11 in a camouflaged livery, summer 1941.

A BA-11D being tested on rough terrain at NIIBT testing grounds, Kubinka, 1939.
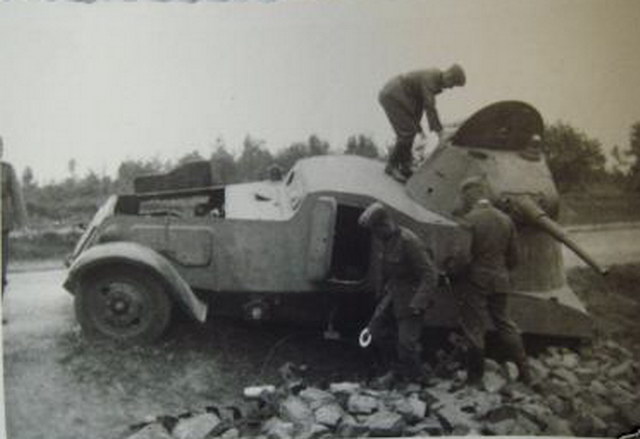 An abandoned BA-11D.
An abandoned BA-11D.
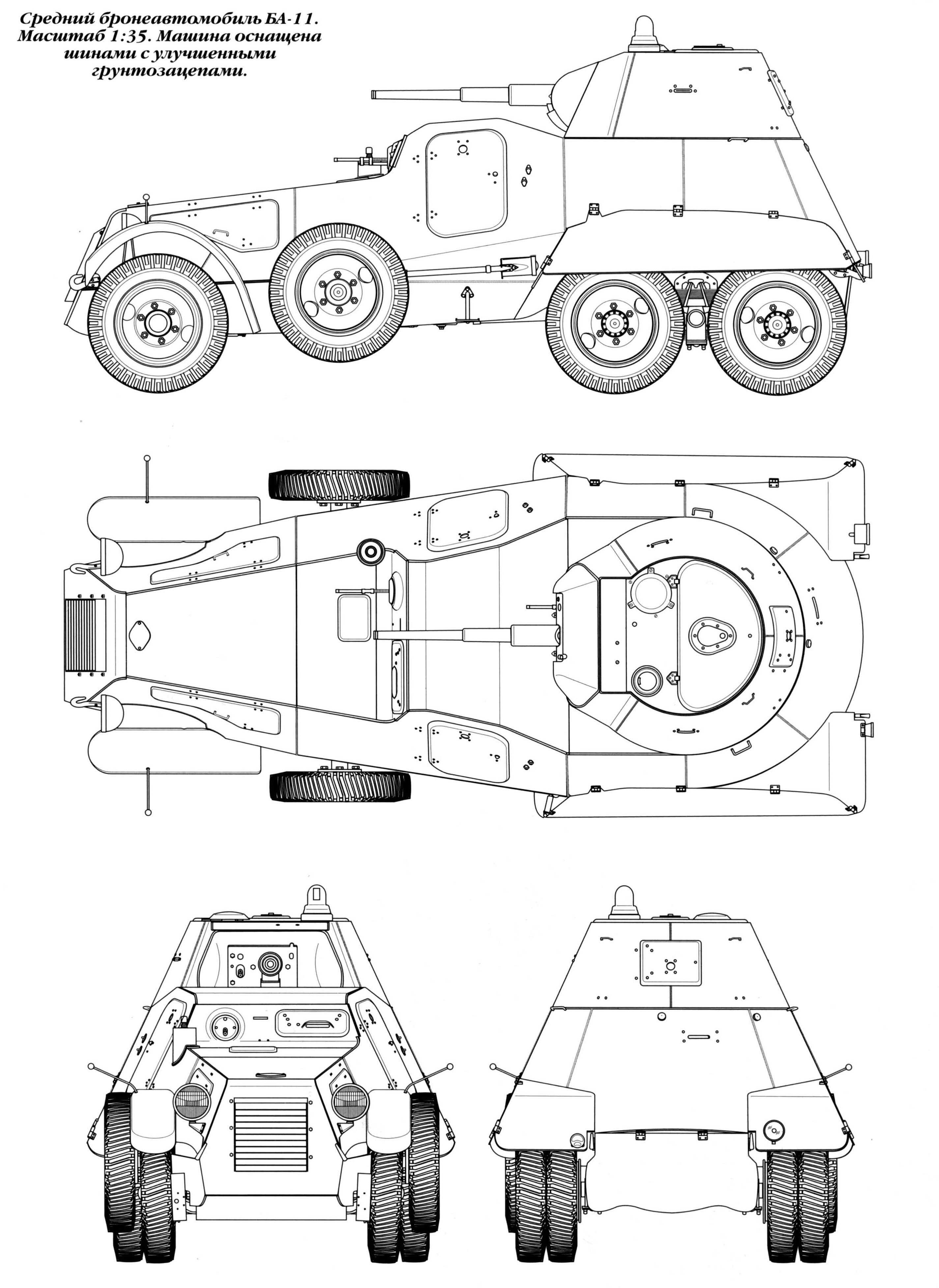
A technical drawing of the BA-11.
Sources and further reading
"Soviet Tanks and Combat Vehicles of WWII" by Steven Zaloga and James Grandsen "Отечественные бронеавтомобили 1905-1941" by A. G. Solyankin ww2 Soviet Tanks Poster
ww2 Soviet Tanks Poster

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

