The T55AM2B is one of the last, but not the very last evolution of the T-55, born in 1959. After the T-54B, the Czech built T55AM and AM2, the AM2B is the final coldwar non-Soviet evolution of the type. Only a handful were so modernized and served in both the East German and Czech armies before the collapse of the Warsaw Pact. Passed to the successor states, the East German ones soon found new international customers (along with the postwar Polish T-55AM2BP): Cambodia (50), Sudan (20), Slovakia still having 206 by 1995.
The best coldwar T-55 ?
Lineage up to the T55AM
The T-54/55 main battle tank family is a large, even plethoric one today. The T-54 was born right after WW2 in large part based on the T-44, a modernized evolution of the legendary T-34 (80,000+ built in both the /76 and later /85 variants). If "only" 1,823 T-44 were build, using a new hull, much lower and new engine, they still constituted a solid chassis onto adapting a more modern turret. The latter, hemispheric, was inspired by the one created for the IS-3 heavy tank, but even further improved. This led to the creation of the T-54-1 model 1948, forebear of a formidable array of "main battle tanks" distributed to half the world and many still in service today.Although the base concept of the T-54 was considered a success, being nimbler and faster than heavy tanks for almost the same firepower and no lack of protection, constraints of the modern battlefield led to its modernization. This called for what was essentially a NBC variants (with tons of other minor improvements) as the 1958 T-55. The later stayed relevant for decades, at least until the 1970s and arrival en masse of the new T-72 MBT. More successful than the T-62, it showed a path of possible improvements on the large park of T-54/55 still in the soviet inventory. If first upgrades were performed in the 1970s notably for protection upgrades, taking as a base the latest T-55A (Ob'yekt 155A), developed in 1961, with an improved NBC protection system (gamma radiation, PAZ/FVU chemical filtration) as well as a new coaxial 7.62 mm PKT machine gun, longer hull, widened hatches, removed hull machine gun, six more main gun rounds.
Older T-54/55s received loader's hatch modified to mount the 12.7 mm DShK machine gun, from 1974 KTD-1/2 laser rangefinder (armoured box over the mantlet), better tracks, KTD-1 "Newa" rangefinder, TSzS-32PM sight, TPN-1-22-11 night sight, improved radio sets. In the 1990s a new set of upgrades, mostly passive and active protection sets, were added. Other producing countries joined the fray, notably Poland, Czechoslovakia, but also East Germany. Following the path of the T-54AM (Ob'yekt 137M, mid-1960s) declined by East Germany as the T-54Z, T-54AZ, T-54AMZ for Zusatzausrüstung, 'additional equipment', the T-55AM appeared with the modifications described above at Uralwagonzavod. However for the Soviet ones, NATO experts prefers to calls it the "Model 1970" as Czechoslovakia by far was the largest producer of the type.
Enters the Czech T55AM
T55AM2
Both Polish and Czechoslovak production of the T-54B under license are indeed known as the T-55AM. This led in Poland to the development of the excellent T-55AM "Merida" with a brand new fire control system and many other imporvements (future dedicated post). In parallel, Czechoslovaia developed the much improved T-55AM2B. Meanwhile Romanian developed its own main variant with the "Volna" fire control system, Czech T-55AM2 with "Kladivo" FCS and ocally upgraded model with "Ciclop" FCS, called the T-55AM2R). Hungary also had its own upgraded T-55AMs in the 1980s (144 with Czech-produced "Kladivo" FCS and other improvements).
To the Czech T-55AM2B
From the Czech T-55AM, was developed the T-55AMB, a properly Czechoslovak upgraded T-55A with homemade laser rangefinder, fire control system and wind sensor mast on the turret roof. The T-55AM1 had the homemade "Kladivo" fire control system (ballistic computer, laser range finder, cross-wind sensor mast) and from there with the T-55AM2, improved on the T-55AM1 by having it fitted with a passive BDD appliqué armour on the turret (horseshoe) plus upper glacis plate and sideplates extensions, improved V-55U engine, R-173P radio system, BDD armour panels semi-reactive armor and new sets of smoke-grenade launchers, additional headlights on front fenders. At last comes the T-55AM2B, an evolution of the previous T-55AM2 which gun had been modified (and electronics reset) to fire tge laser-guided 9M117 "Bastion" (AT-10 Stabber) ATGM as well as the 1K13 BOM gunner's sight. The latter was also declined into command variants.The T-55 in East Germany

East Germany obtained 202 T-54s ordered in 1956, 488 T-54As/T-54AMs (from Poland) until 1964, 1766 T-55s and T-55As ordered in 1964 from Czechoslovakia, delivered between 1964 and 1980 and an additional 333 T-55s and T-55A(P)s ordered from Poland, last delivered in 1973. East Germany also doubled down with Czechoslovakia with 362 VT-55s from 1964 until 1969. It's not difficult to understand the preferrence of East Germany for Polish or Czech vehicles, as quality was favored over the Soviet production, generally seen of much lower quality.
Thus in the 1980s, East Germany order to Czechoslovakia the AM2B, which was used as a template for local upgrades, ported on the park of existing T-55As. In the German case they were completed however with the bin on the left-hand-side of turret. This bin is typical of Czech-built T-55s and best way to distinguish from Soviet production. The rest is identical. All in all, Czechoslovakia produced some 11,000 T-54/55s between 1957 and 1983, so two years after USSR stopped, four years after Poland. It was seen at the time cheaper to upgrade the T-55 than to develop a brand new MBT.
Design of the T-55AM2B
T55AM2 antenna IR searchlight turret
The Czech T-55AM2B is essentially a much improved T-55AM2.
General design and protection
The general design was inherited from the T-55B, itself from the T-55A, T-55 and T-54. The hull shape was the same (albeit a tad longer), as the turret, with minot improvements for better NBC protection. Sealing, filter, overpressure, new fire suppression systems were all incorporated. For more details over the design, check the T-54/55 articles seen above.It's on the chapter of protection that the Czech T-55AM2B improved the most:
-Passive BDD appliqué armour for the turret of the "horseshoe" type.
-Hull front upper glacis plate BDD armor caisson
-Sideplates fitted with extensions, protecting the catwalk fuel tanks.
The BDD armour panels are basically large shaped armoured steel boxes, filled with Penpolyurethane with cavities which can be filled with water or sand, for additional protection but also interleaved with thin HHS steel plates. The BDD semi-reactive armor has been evaluated by NATO as providing the virtual same protection as:
-120mm of RHA protection against APDS rounds
-200-250mm of protection against HEAT ammunition
This made the AM2B on par with the T-72 in terms of passive protection.
And for active protection, these T-55AM2Bs shars a cluster of 8 smoke-grenade launchers on the right-hand-side of the turret (Czech variant) or lef-side (East German variant), the other being occupied by the large storage bin, again inverted between the two versions.
Mobility
The T-55AM2 and AM2B shares the same improved V-55U engine, with an integral supercharger, delivering 620 hp.Better armament and FCS
The AM2 retook the AM1 improvements, consisting of the Czechoslovak-produced "Kladivo" fire control system coipled with a homemade ballistic computer and new laser range finder, mounted on top of the gun. The turret rear also received the cross-wind sensor mast mounted on rear of the turret roof.The "B" difference in the name indicates the addition of the laser-guided 9M117 "Bastion" (AT-10 Stabber) ATGM capability via the main gun, as well as adoption of the 1K13 BOM gunner's sight in place of the original TPN-1M-22 sight.
The T-55AM2B also has the improved R-173P radio system. For extra visibility at night, the T-55AM2 was also fitted with additional headlights on the front fenders, repeated on the AM2B.
Gallery
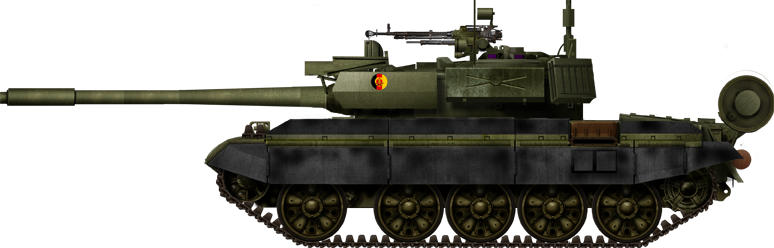
East German T-55AM2B

Czech T55AM2B Kladivo

Czech camouflaged T55AM2B Kladivo

Czech T55AM2
T-55AM2 National Museum Military History Sofia


Sri Lanka T55AM2
Read More
AM2 on armedconflicts.comAM2B on recomonkey.com
Kladivo on scalemates.com
army-guide.com
T-55 (wiki)
T-55 variants
T55 on TE

Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army
Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com


