Charron, Girardot & Voigt
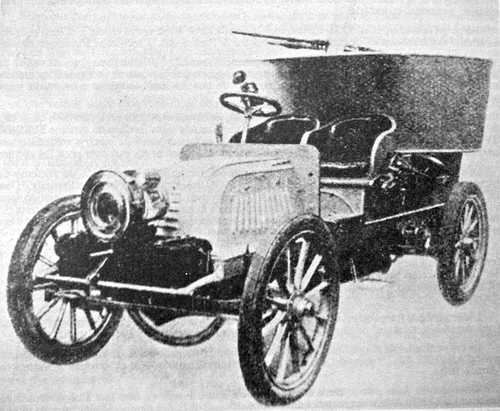
Charron, Girardot, and Voigt were three former cycling champions, associated in 1901 to produce their first four cylinder, 3300 cc, chain transmission car at Puteaux, near Paris. The firm first known as CGV, or more simply "Charron" built several models, including the world's first eight-cylinder in line in 1903. In 1906 the first drive shaft transmission model was out. However, the company was acquired by a British group and renamed Charron Ltd after the departure of Girardot. During the Great War, the firm was one of the few producing vehicles, all having in common an awkward engine cooling configuration, as the radiator was placed behind the engine. Charron disappeared following the 1929 crisis.The first modern armoured car built in serie
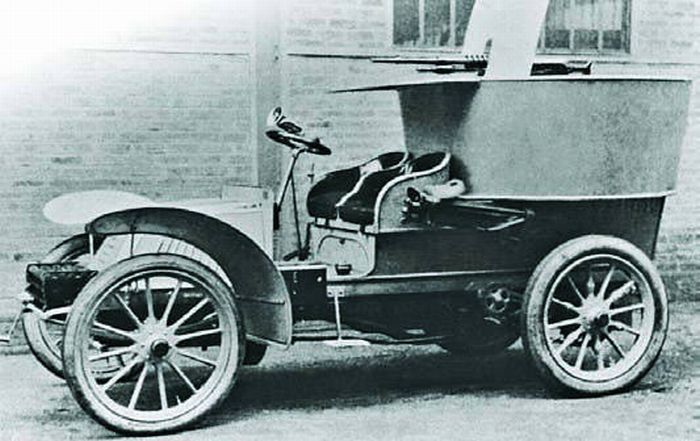
In 1902, the company developed a partially armored model for the army's needs, which was the world\'s first true production armored car. It was equipped with an armored, 3 mm (0.12 in) thick "bath-tub" style gunner platform, located at the rear. The Hotchkiss standard machine gun had some traverse and elevation which did not require a true turret. But the vehicle was essentially unarmored. In 1903 this model was tested by the French military, but not accepted in service. Later, two improved models from a Russian design were presented in 1904 and received positive results as one was purchased by the army and sent to Morocco. The second was acquired by its original customer, Russia and used against rioters in St. Petersburg, with great success.A Russian design
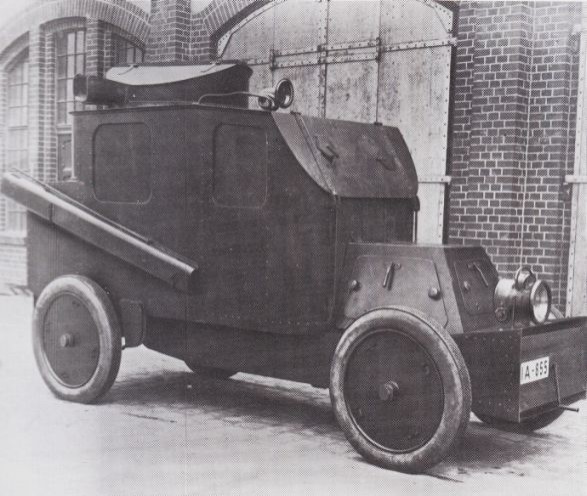
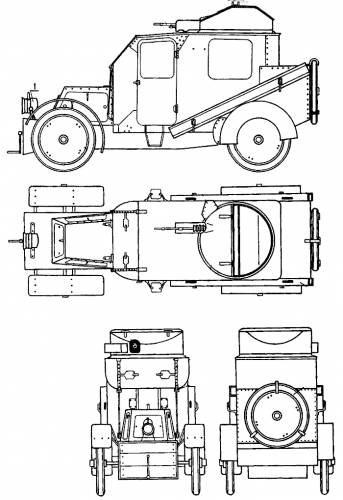
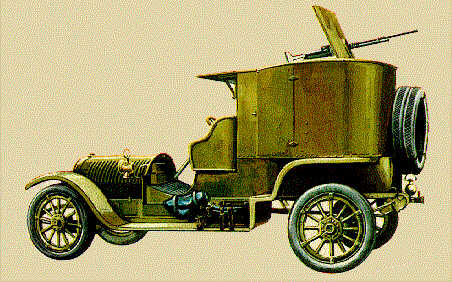
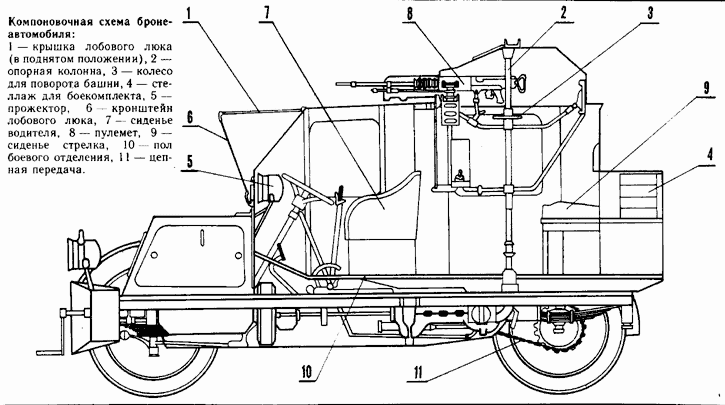
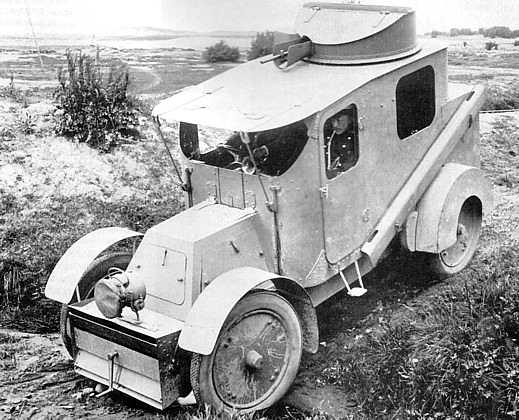
Georgian engineer and officer M.A. Nakashidze designed the first Russian armored car back in 1905, full of practical experience gained during the Russo-Japanese war. This was a completely enclosed model, both engine and crew compartment, with 4-8 mm (0.16-0.32 in) of armor, a combat weight of 2.7 tons, a 360° revolving turret, and capable of 50 km/h (31 mph) on flat ground. It was accepted by the Russian War Ministry for service but still, no local factory was able to built it. At the same time, Paul Daimler built the Austro-Daimler armoured car, which was the very first with a revolving turret, and sloped armor. It was never ordered by the Austro-Hungarian army though, but was quite influential.The Nakashidzz design was subcontracted to the French Charron carmaker. Commandant Guye adapted the model from the 15 CV touring car in 1906, which had also a 6 mm (0.24) thick hinged front armored panel, and four large windows with steel panels which slid up to cover them. The main armament was a model 1902 air-cooled Hothckiss machine-gun protected by a U shaped shield. The wheeltrain was unchanged: four spoked wheels, protected, and leaf-spring suspensions. The tires were filled by a liquid and could still run 10 minutes after being shot at. Another innovation was an engine starter from the inside. The front low-slung radiator was a common feature on CGV models. There was also a single gas headlight mounted on the radiator and a spotlight mounted inside the body. Another characteristic were the two removable steel channels placed over the rear wheels for crossing ditches.
The prototype performed well during the autumn 1906 maneuvers. In Russia, the twelve built and shipped by rail in 1908 were called the "Nakashidze-Charron". Two seemed to "disappear" en route in Germany, apparently seized and tested thoroughly by the German army.
Wartime use
Four vehicles were used by the French army at the outbreak of WWI, mainly to hunt enemy observation balloons. Tests were even performed with 75 mm (2.95 in) AA guns. However the CGV had a poor power-to-weight ratio and thus limited mobility. But the concept was an instant success. Despite the fact that Charron stopped any development of this model to concentrate on civilian vehicles, other companies like Hotchkiss and Panhard, opened enthusiastically to this new business, building close copies of the Charron. They were followed by De Dion Bouton, Latil, Renault and Peugeot in 1914-15.Four Hotchkiss copies of the CGV were delivered to Turkey in 1912, and most of these came into rebel hands and were then turned by the Greeks against their former owners.
Links about the Charron
The Charron on WikipediaCharron model 1905 and other early WWI armored cars (in French)
| Charron specifications | |
| Dimensions | 4.8 x 1.70 x 2.4 m (15.75x5.58x7.87 ft) |
| Total weight | 3 tons |
| Crew | 3-4 (driver, commander, gunners/loader) |
| Propulsion | 4-cyl Gas. CGV, 35 bhp (26 kW) |
| Top speed (road) | 45 km/h (28 mph) |
| Range | Around 100 km (62 mi) |
| Armament | 1 Hotchkiss M1902 machine gun |
| Armor | 4 to 8 mm (0.16 to 0.32 in) |
| Total production | 16 between 1902-1906 |

The Great War
 Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary Belgium
Belgium British Empire
British Empire France
France German Empire
German Empire Italy
Italy Russia
Russia USA
USAWW1 tanks posters